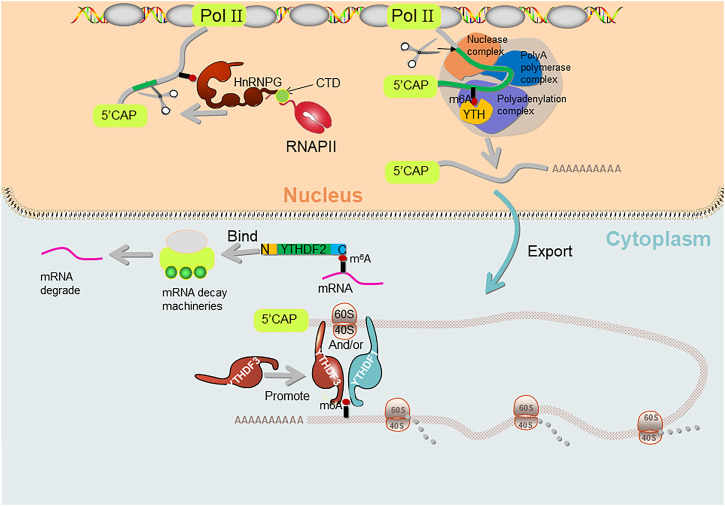
FIGURE 2.
The molecular mechanisms of how m6A affects splicing/polyadenylation/translation. YTHDF1 and YTHDF3 regulate m6A both individually and together. hnRNPG binds to m6A-containing 3′-terminal mRNA and interacts with 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits to regulate mRNA translation, and YTHDF3 also facilitates this process. hnRNPG binds to m6a-containing pre-mRNA and interacts with RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) phosphorylated carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II, which in turn regulates alternative splicing of mRNAs. C-YTHDF2 selectively recognizes m6A-containing mRNAs, while N-YTHDF2 on the other side binds to mRNA decay machineries and regulates mRNA degradation. YTH domain binds to the m6A-containing pre-mRNA and regulates the length of the 3′ UTR through polyadenylation complexes.