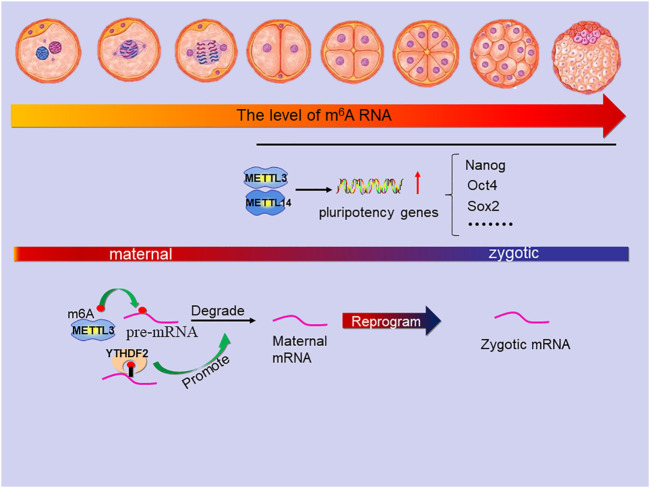
FIGURE 7.
The main role of m6A in the stage of embryonic development. The level of m6A modification increased slowly in mouse 2-cell, 4-cell and 8-cell embryos but suddenly increased significantly in the transition period from morula to blastocyst which is due to the METTL3 and METTL14 active transcription of many pluripotency genes (includes Nanog, Oct4, Sox2 and so on). In the MZT, METTL3 mediates the m6A modification on pre-mRNA to degrade maternal mRNA and YTHDF2 can promote the process, which is reprogramming zygotic mRNA for zygotic development.