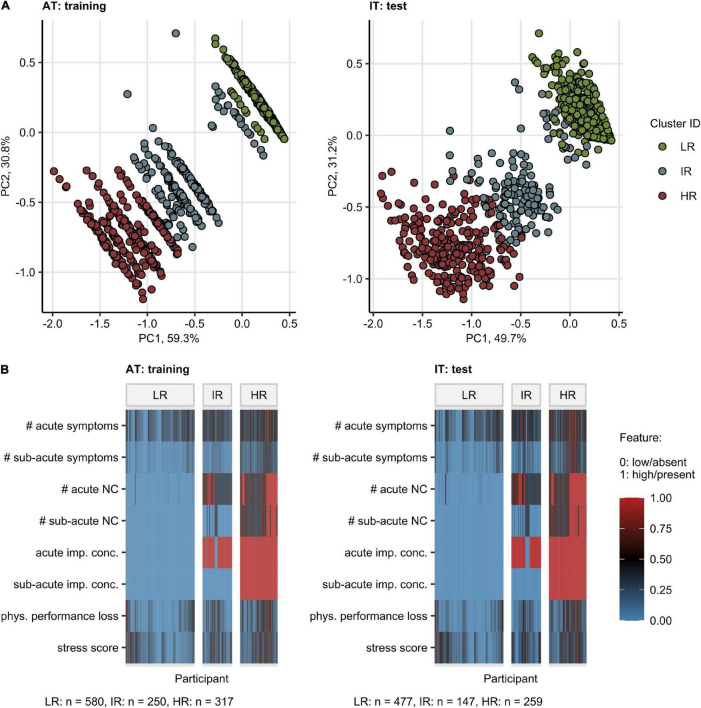
FIGURE 4.
Clustering of the study participants by the most influential factors affecting the mental health and quality of life scoring. Study participants were assigned to the Low Risk (LR), Intermediate Risk (IR), and High Risk (HR) subsets by clustering in respect to the most influential factors for the mental health and quality of life scoring (Figure 2B). Numeric variables were minimum/maximum normalized prior to modeling. The procedure in the training Austria (AT) cohort involved the self-organizing map (SOM, 13 13 hexagonal grid, Manhattan distance between participants) and the hierarchical clustering (Ward D2 method, Manhattan distance between the SOM nodes) algorithms. Assignment of Italy (IT) cohort participants to the clusters was accomplished by the k-nearest neighbors classification. The numbers of participants assigned to the clusters are presented in (B). (A) Cluster assignment of the participants in the 3-dimensional principal component (PC) analysis score plot. The first two components are shown. Percentages of the data set variance associated with the particular PC are presented in the plot axes. (B) Heat map of the minimum/maximum-normalized clustering features. NC: neurocognitive symptoms, imp. conc.: impaired concentration, phys.: physical, #: number of.