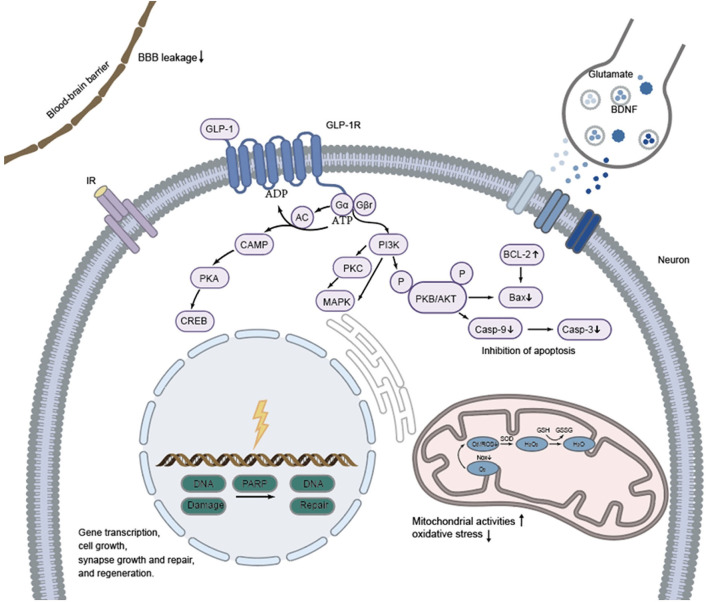
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanisms of neuroprotective efficacy exerted by GLP-1 and GLP-1RAs against stroke in animals. Effects of GLP-1 and GLP-1RAs are mediated by binding to a specific, seven-transmembrane GLP-1R which is positively coupled to the adenylyl cyclase (AC) system. GLP-1 and GLP-1RAs acts directly by the cAMP/PKA signal pathway to facilitate gene transcription, synapse growth and repair, cell growth, and regeneration. The Gβγ dimer stimulates the PI3K, which then activates PKB/AKT pathway to inhibit apoptosis. In addition, GLP-1 and GLP-1 RAs play a role through reduction of blood-brain barrier leakage and neurotransmitter transmission among synapses as well.