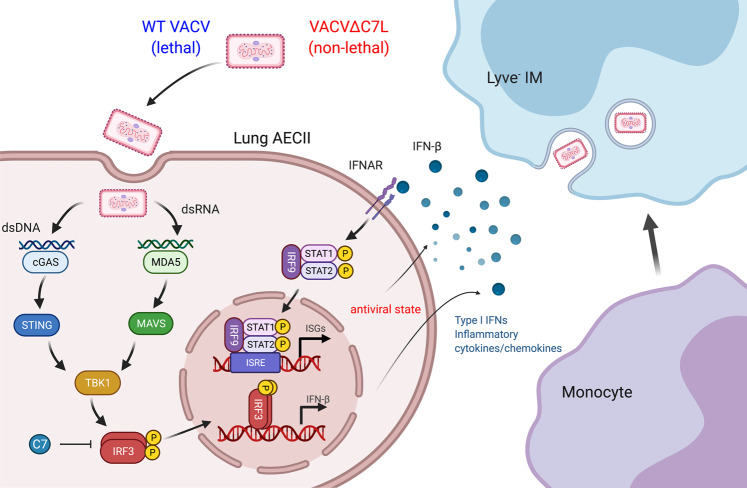
Fig. 7. Model of lung innate immune system to protect against vaccinia virus pulmonary infection.
Vaccinia C7L encodes a virulence factor. Whereas intranasal infection of WT VACV causes lethality in mice, VACV∆C7L infection is non-lethal. Here we show that C7 blocks the phosphorylation of transcription factor IRF3, which is critical for the induction of IFNB gene expression. VACV∆C7L infects lung AECIIs and triggers IFN-β production via activating the cytosolic DNA and dsRNA-sensing pathways that are dependent on MDA5 and STING. IFN-β-IFNAR signaling on lung AECII further strengthens antiviral effects via the induction of IFN-stimulated genes. Under the influence of various cytokines and chemokines produced by lung AECIIs, CCR2+ inflammatory monocytes further differentiate into Lyve1- IMs to fortify host immunity.