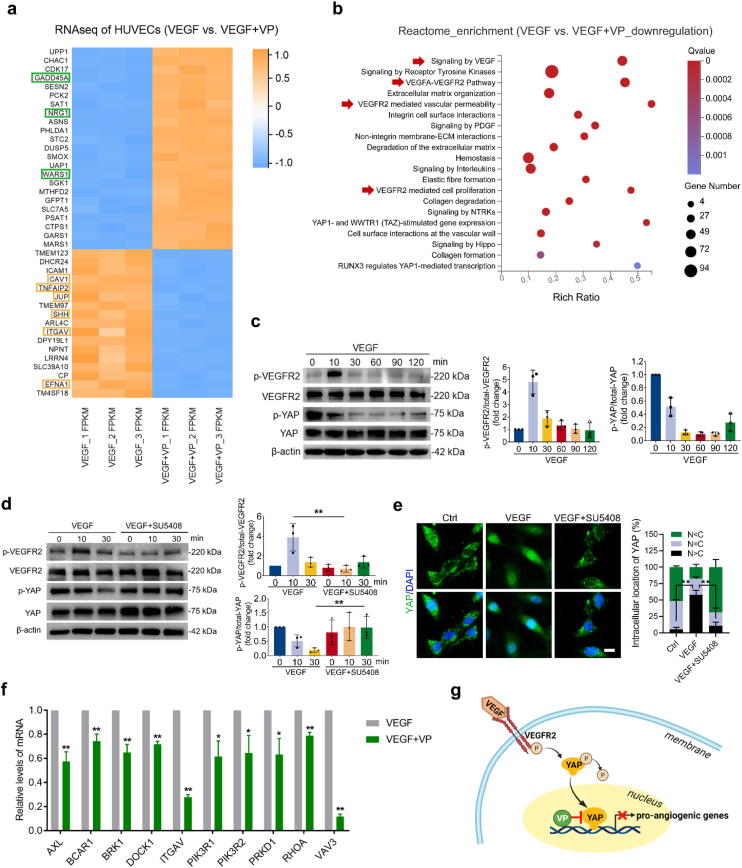
Fig. 7.
VP inhibits VEGF-induced VEGFR2-YAP signaling. (a) Heatmap showing RNA-seq expression of the top 40 marker genes identified from VEGF-treated HUVECs and VEGF + VP-treated HUVECs. Green box: genes that negatively regulate angiogenesis, yellow box: genes that positively regulate angiogenesis. (b) Reactome enrichment analysis of downregulated genes in HUVECs treated with VEGF + VP compared with VEGF-treated cells. The red arrowhead indicates biological processes related to VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling. (c) Western blotting detection and quantification of VEGFR2 phosphorylation and YAP phosphorylation in HUVECs incubated with VEGF (200 ng/mL) for the indicated time points (n = 3). (d) VEGFR2 phosphorylation and YAP phosphorylation in HUVECs pretreated with or without SU5408 (a VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor) and then incubated with VEGF for the indicated lengths of time (n = 3). **P < 0.01 by Student's t-test. (e) Subcellular localization and quantification of YAP in HUVECs pretreated with SU5408 for 2 h and then stimulated with VEGF for 6 h, as illustrated by immunofluorescence (n = 3). N: nucleus, C: cytosol. Scale bar: 10 μm **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA followed by LSD post hoc test. (f) qPCR validation of the mRNA expression of genes related to the VEGF receptor signaling pathway identified by RNA-seq in HUVECs (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Student's t-test. (g) Schematic depiction of VP inhibition of the VEGFR2-YAP signaling axis.