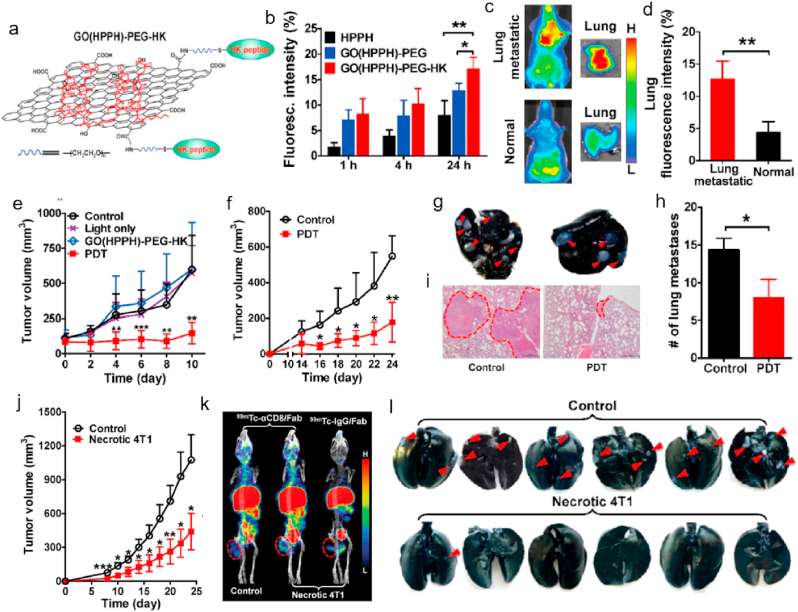
Fig. 5.
a. Preparation of GO(HPPH)-PEG-HK nanocomposite. b. The in vitro cellular uptake of different formulations by 4T1 tumors after incubation for different time. In vivo accumulation (c) and quantitative analysis (d) of GO(HPPH)-PEG-HK in lung in 4T1 tumor-bearing and normal BALB/c mice at 24 h post-injection. e. Tumors volume of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice after different treatments (PBS, light only, GO(HPPH)-PEG-HK) without light and GO(HPPH)-PEG-HK) with light) recorded every 2 days. f. Tumor volume of the second 4T1 tumor in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice after indicated treatments. Images (g) of India ink-filled lungs, histogram of metastatic lesions in the lung (h), and H&E staining of the lung tissue section (i). j. Tumor volume of subcutaneous 4T1 tumors in mice with (control) and without prophylactic vaccination using necrotic 4T1 cells. k. SPECT/CT imaging of 99mTc-αCD8/Fab and 99mTc-IgG/Fab in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice with (control) and without prophylactic vaccination using necrotic 4T1 cells. Tumors are marked by dashed circles. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. l. Quantitative analysis of tumor metastasis lesions in lungs of mice with (control) and without prophylactic vaccination using necrotic 4T1 cells. Cited and reproduced from the reference [99].