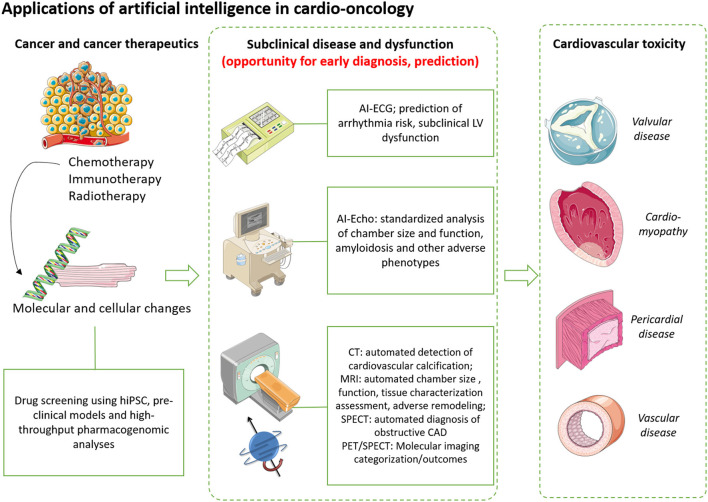
Figure 4.
Applications of artificial intelligence, big data in cardio-oncology. Artificial intelligence (AI) can improve our understanding of the early molecular and phenotypic changes that occur prior to the development of clinical cancer therapeutics-related cardiac dysfunction. Machine learning approaches enable high-throughput screening of novel therapeutics using preclinical models, such as induced pluripotent stem cells as well as in silico simulations using libraries of drugs and molecular targets. In the clinical setting, AI can improve risk prediction of left ventricular dysfunction, arrhythmias as well as facilitate accurate and standardized assessment of chamber size, function and coronary calcification, all hallmarks of cardiovascular disease that can be caused or exacerbated by cancer therapeutics. Therefore, AI offers an opportunity for early diagnosis and deployment of strategies to prevent the progression to overt cardiovascular disease. Images have been reproduced under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License from smart.servier.com. CAD, coronary artery disease; CT, computed tomography; ECG, electrocardiography; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; LV, left ventricular; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SPECT, single photon emission computed tomography.