Figure 2.
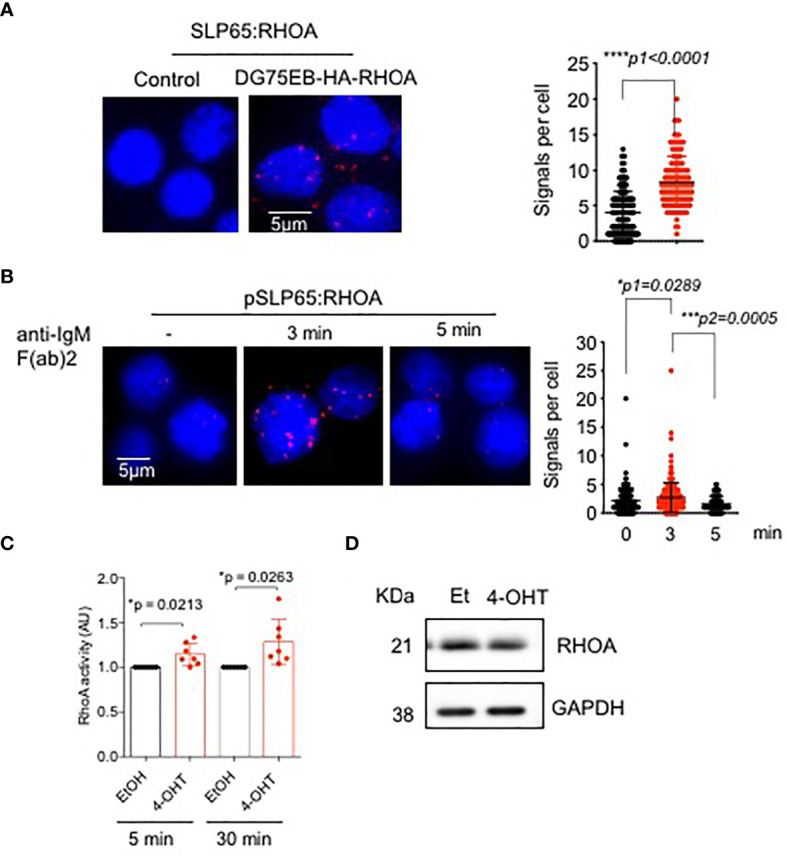
SLP65 interacts with RHOA and regulates its activation. (A) Left- PLA showing the association of SLP65 and RHOA in DG75EB/HA-RhoA cell line. Only secondary antibodies are used in the controls. Close proximity is shown as red dots. Right- quantification of number of signals per cell, error bars represent mean ± SD. Unpaired t-test, two-tailed. (B) Left- PLA showing the association of RHOA with phosphorylated SLP65 in DG75EB/HA-RhoA cell line upon BCR stimulation. Cells were stimulated with anti-IgM F(ab)2 antibody for the specified time period. Right- quantification of number of signals per cell, bars represent mean ± SD. Unpaired t-test, two-sided. (C) Detection of total cellular RHOA activity by G-LISA RHOA activation assay. Reconstituted bone marrow derived pre B cells from TKO mice were treated with ethanol (control) or 4-OHT to induce SLP65 for the indicated time point. Equal amounts of cell lysates from control and 4-OHT treated cells were used for the assay. Statistical analysis: one sample t test. (D) Western blot analysis for the detection of RHOA upon SLP65 activation in TKO cells. The cells were reconstituted with µ-heavy chain, λ5 and inducible SLP65-ERT2 construct and then induced with 2µM 4-OHT or Et for 30 min to activate SLP65. GAPDH is used as loading control. *p<0.05, ***p< 0,001, ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant.
