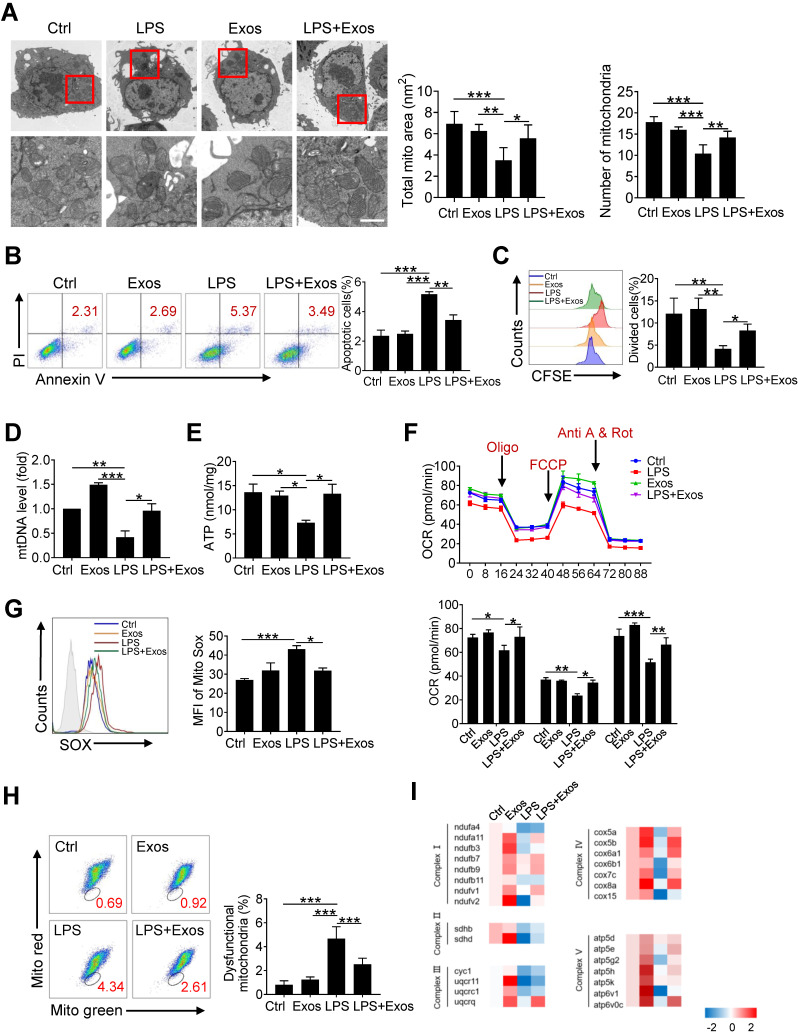
Figure 3.
Transferring of mitochondrial component through AdMSC-Exos improves macrophage mitochondrial function. (A) Representative transmission electron micrographs (TEM) showing mitochondrial amount, morphology and cristae. The histogram represents the quantification of the size and number of mitochondria. Scale bar, 1 μm. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of the effect of exosomes on MH-S cell apoptosis. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of the effect of exosomes on the proliferation of MH-S cells. (D) Mitochondrial DNA expression in MH-S cells. (E) Expression of mitochondrial ATP production in MH-S cells. (F) Effects of AdMSC-Exos on oxidative phosphorylation of MH-S cells detected by Extracellular flux analysis. (G) Flow cytometry and quantification of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels by staining with Mito Sox. (H) Flow cytometry of mitochondria staining with Mito Tracker Red and Mito Tracker green (Green+/Red-). (I) Heatmap showing the expression of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex-related genes in MH-S cells detected by qPCR. Primer sequences are reported in Table s1. All the data are expressed as the mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.