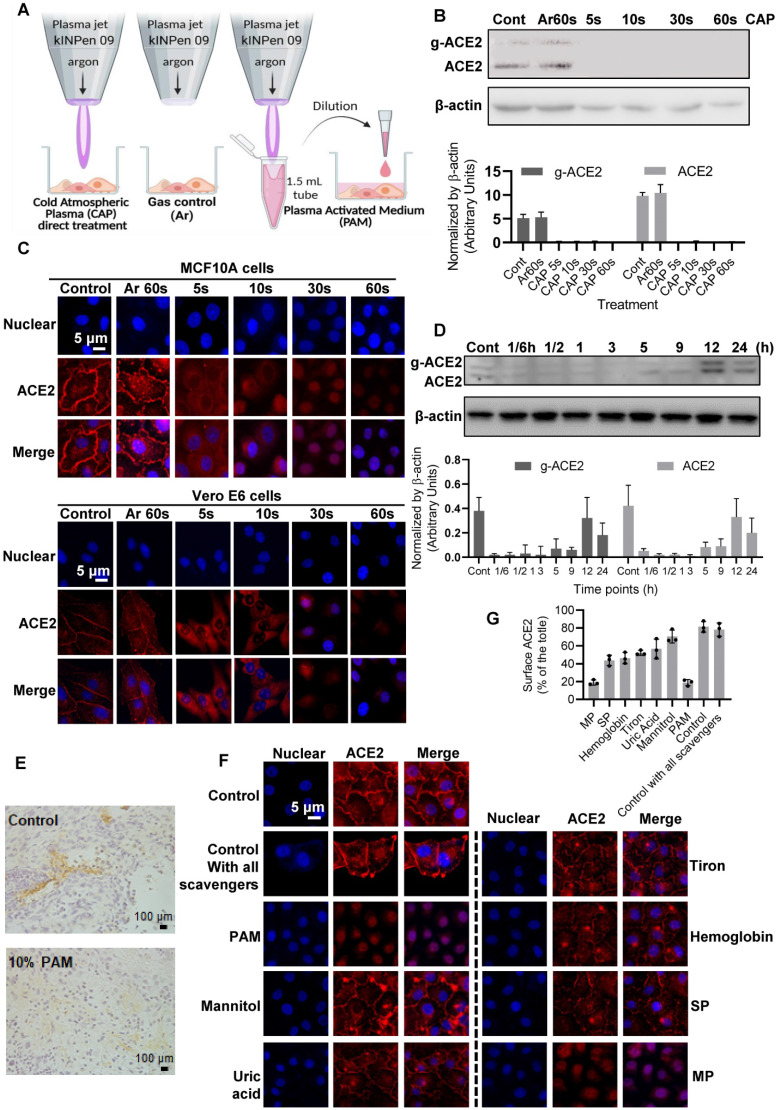
Figure 4.
ACE2 expression and location after PAM treatment and examination of the active CAP components triggering such an effect. (A) Cells are treated directly with CAP or indirectly with PAM or gas control (Ar). (B) Western blot and quantification of ACE2 after direct CAP exposure as indicated. (C) Immunofluorescence images of ACE2 after direct CAP exposure in MCF10A and Vero E6 cells. (D) 30 s-PAM for 60 s treatment and wash with PBS. Refresh with 10% FBS RPMI-1640 medium for 1/6, 1/2, 1, 3, 5, 9, 12 and 24 h. The ACE2 protein expression levels were detected by Western blot. (E) IHC results from in vivo mouse experiments. Surface ACE2 expression as represented by glycolyzed ACE2 in cells with and without 10% PAM treatment using the SUM159PT-inoculated mice model. (F) Immunofluorescence images showing ACE2 localization and expression after direct CAP exposure for 30 s when different ROS scavengers were used, and signal quantification. In this assay, 200 mM mannitol, 100 μM uric acid, 20 mM tiron, 20 mM hemoglobin, 10 mM sodium pyruvate and 1 mM monopotassium were used to quench hydroxyl radical, ozone, superoxide anion, nitric oxide, H2O2, and e-, respectively. The second control in (A) and (B) was '60 s Argon (Ar) exposure'. The dosing effect of CAP was measured under different treatment durations in the form of plasma activated medium (PAM). MCF10A cells were used. 'g-ACE2' is short for 'glycosylated ACE2' and 'ACE2' represents 'non-glycosylated ACE2'. Scale bar: 5 μm. (G) The quanlification data of (F).