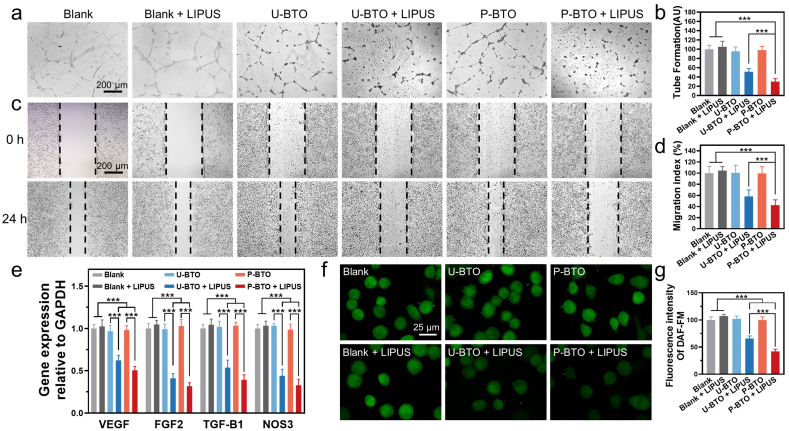
Fig. 2.
Effect of wireless electrical stimulation on HUVEC behavior in vitro. (a, b) Tube formation assay and quantitative analysis. Data are mean ± s.d. of biological replicates (n = 4). (c, d) Representative migration images and migration index statistics of HUVECs at 0 and 24 h. Data are mean ± s.d. of biological replicates (n = 4). (e) Expression of the angiogenesis-related genes in HUVECs after 48 h. Data are mean ± s.d. of biological replicates (n = 6). (f, g) Intracellular NO staining and quantitative analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 or ***p < 0.001. Enhanced wireless electrical stimulation generated by P-BTO nanoparticles under LIPUS significantly inhibited the recruitment of endothelial cells into blood vessels by downregulating the eNOS/NO pathway.