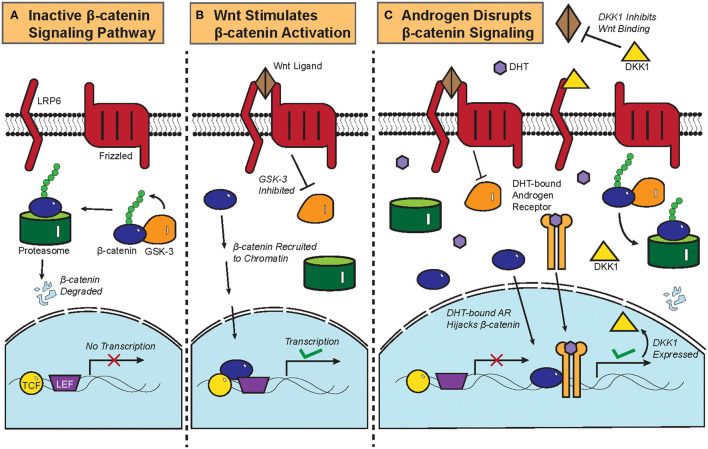
Figure 2.
Biochemistry of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and its crosstalk with androgen. (A) Constitutive phosphorylation of β-catenin by glycogen synthase kinase 3B (GSK-3B) and subsequent proteasomal degradation of β-catenin in the absence of Wnt ligand. (B) Binding of Wnt ligand to Frizzled and Low-Density Lipoprotein-Related Protein (LRP) and the resultant inactivation of GSK-3B and its phosphorylation of β-catenin, which is then translocated to the nucleus to initiate the transcription of target genes. (C) DHT-activated AR can recruit β-catenin as a coactivator to stimulate the expression of DKK1, a competitive antagonist of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Crosstalk between DHT-activated AR and β-catenin thus leads to downregulation of β-catenin target genes.