Fig. 3.
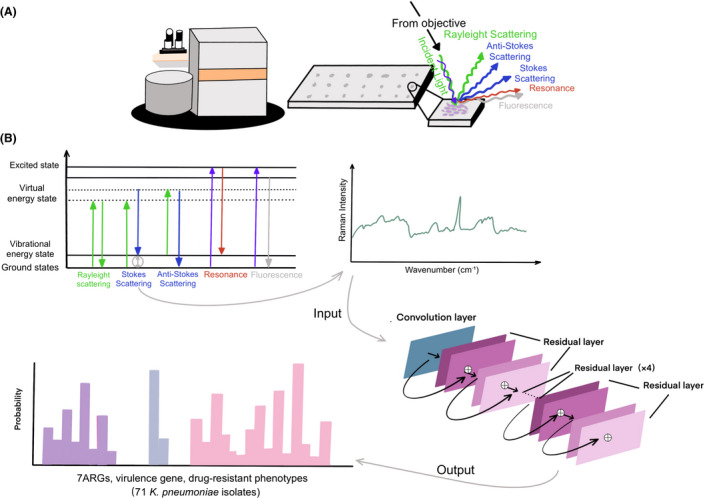
Summary schematic of confocal Raman microscope techniques including sample preparation to spectral analysis and the construction of ResNet taxonomic model.
A. The K. pneumoniae lawn was smeared onto the stainless‐steel plate for Raman spectral collection. The schematic identifying light scattering after laser exposure on a sample surface. When the electrons are excited to virtual energy levels, it can return to the original energy level by emitting a photon of light, known as Rayleigh scattering, or it can undergo an energy shift, known as Stokes scattering or anti‐Stokes scattering. Resonance Raman scattering and fluorescence can occur when electrons are excited to electronic energy levels.
B. The antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), virulence genes and antibiotic susceptibility are identified and analysed using convolutional neural network. Using a one‐dimensional residual network with 25 total convolutional layers (see Section 2 for details), Raman spectra are analysed to predict the existence of ARGs and virulence genes or the drug‐resistant phenotypes.
