Fig. 2.
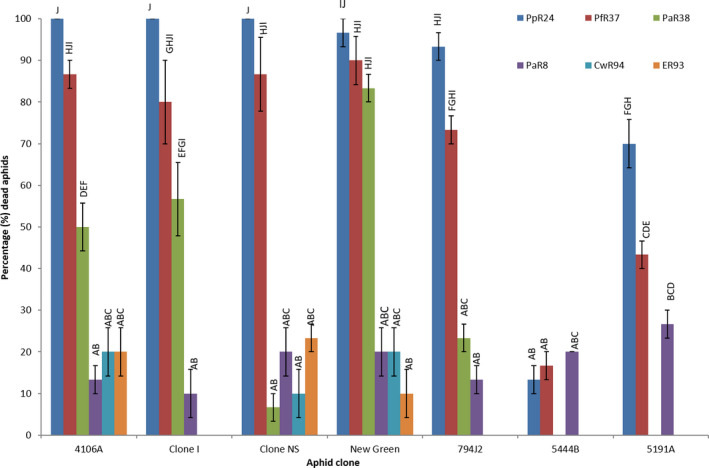
Assessment of aphid mortality caused by selected bacteria. Mortality assay showing the percentage of dead aphids (N = 10) at 48 h after ingestion of artificial diet inoculated with cells of various bacterial species (107 CFU ml−1). Error bars represent standard error of the mean of three biological replicates. ANOVA detected statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) and comparison of means by Tukey–Kramer HSD were shown as letters (where different letters on the graphs indicate statistically significant differences). Aphid clones – three susceptible clones ‘4106A‐SUS 1’, ‘4225B‐SUS 2’ and ‘Clone‐NS SUS 3’ and four resistant clones ‘New green – RES 1’, ‘794J2 – RES 2’, ‘5191A – RES 3’ and ‘5444B – RES 4’. Bacterial strains tested – Pseudomonas fluorescens PfR37, P. fluorescens PpR24, Pantoea sp. PaR8, Pantoea agglomerans PaR38, Enterobacter sp. CwR94 and Enterobacter sp. ER93.
