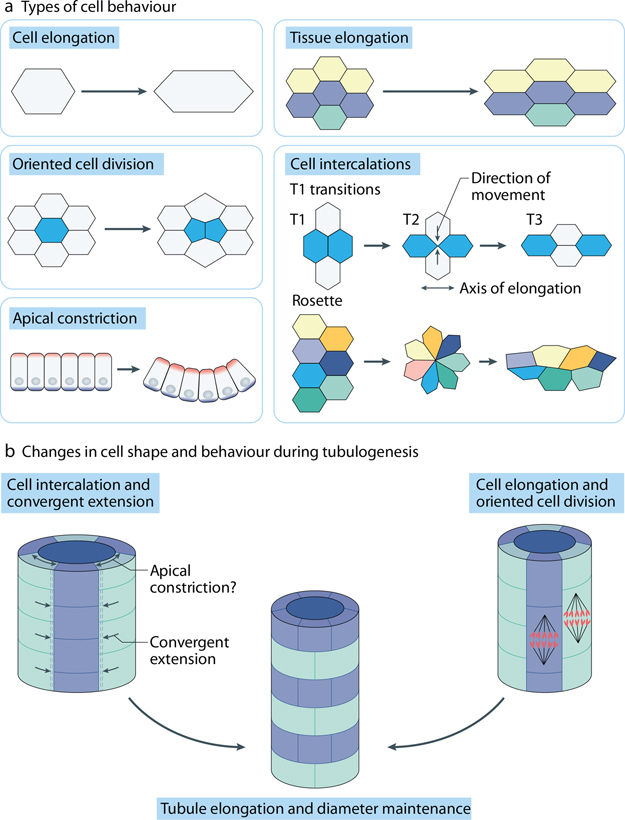
Figure 2: Cell behaviors during morphogenesis.
(A) Types of individual and collective cell behaviors that affect tissue architecture during morphogenesis. Cell elongation and oriented cell divisions act to promote tissue extension or orchestrate branching events. Cell intercalations are mediated by so called T1 transitions that involve four neighboring cells and by more complex intermediate ‘rosettes’ that include 5 or more cells. Apical constriction affects the curvature of the folding tissue and can promote neighbor cell exchanges. (B) Examples of cell behavior relevant to the formation of renal tubules. Both cell elongation and oriented cell divisions can stimulate tubule lengthening. Cell intercalations that accompany convergent extension rely on elongation and polarization of cells in the medio-lateral direction perpendicular to the tubular axis. Both cell intercalation and apical constriction reduce tubule diameter and lead to tubule elongation. Oriented cell divisions enable incorporation of a daughter cell along the tubular axis, facilitating tubule lengthening