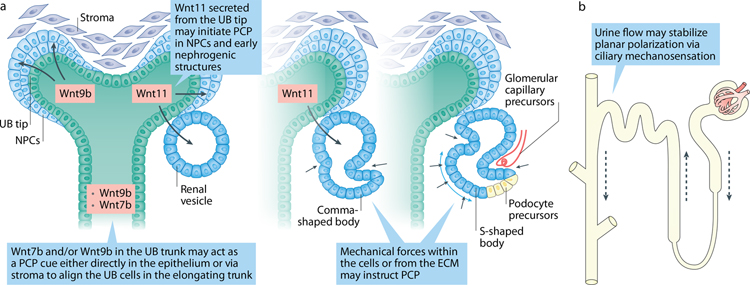
Figure 5. Potential instructive cues establishing PCP during kidney development.
The origin of PCP in early tubules is unknown, however, several molecules may potentially act as cues to initiate PCP in early nephrogenic structures. E.g. Wnt11 that expresses at the UB tip directs polarized NPC behaviors as they epithelize and transform into pre-tubular aggregates and renal vesicles. The link between apical-basal and PCP networks may coordinate establishment of planar polarization in the earliest structures. In the trunk, Wnt9b or Wnt7b may act locally in the UB trunk or non-autonomously on the cells adjacent to developing tubule to stabilize polarity of proliferating UB cells. Additionally, mechanical forces within the cells and/or from the ECM may provide polarity cues as comma- and S-shaped bodies undergo significant stretching and invagination. Onset of urine formation at E15.0 in the mouse nephron may provide further cues via ciliary mechanosensation to stabilize planar polarization along the growing tubule.