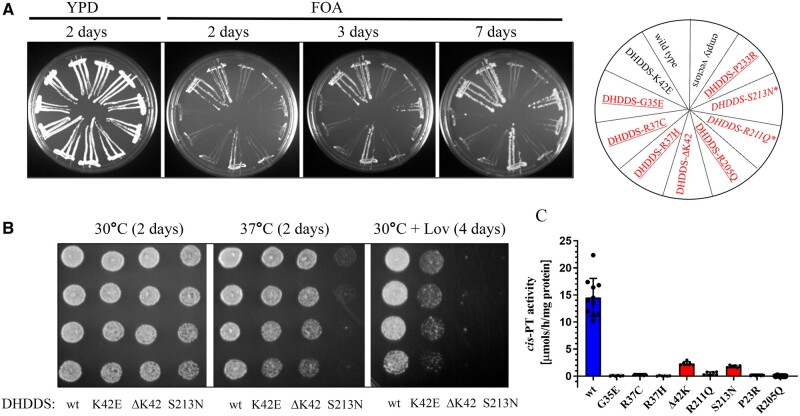
Figure 7.
Functional analysis of DHDDS mutants in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae complementation system and measurement of hcisPTase activity. (A) The rer2Δ, srt1Δ, nus1Δ triple deletion strain expressing G. lamblia cis-PT from URA3 plasmid was co-transformed with the LEU2 and MET15 plasmids overexpressing wild-type or mutated variant of DHDDS with wild-type NgBR. The cells were streaked onto complete plates (YPD) or synthetic complete medium containing 1% fluoroorotic acid (FOA). The Ura3 protein, which is expressed from the URA3 marker present in the plasmid, converts FOA to toxic 5-fluorouracil. The growth of cells was monitored over time to assess phenotypic differences. The combination of alleles affecting growth is marked with asterisks, and the combination of alleles not supporting growth is underlined. Mutated alleles expressed in patients are indicated in red. (B) Yeast cells lacking endogenous yeast cis-PTase subunits but co-expressing human DHDDS under native RER2 promoter from centromeric plasmid and NgBR were grown overnight in liquid YPD medium. Cells were diluted to a final concentration of 0.8 optical density units per 1 ml in water, and then 3 μl of each suspension and three subsequent 10-fold serial dilutions were each spotted onto YPD or YPD supplemented with 250 µg/ml of lovastatin (Lov). Cells were incubated at 30 and 37°C up to 4 days to assess phenotypic differences. (C) Cis-PTase activity was measured using purified wild-type DHDDS/NgBR complex or heteromeric complex formed with DHDDS disease mutants as described in the 'Materials and methods' section. Each mutation exhibits reduced cis-PTase activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. G35E, R37C, R37H, R205Q and P233R mutations result in a complex with activity at the detection threshold. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of at least six independent measurements.