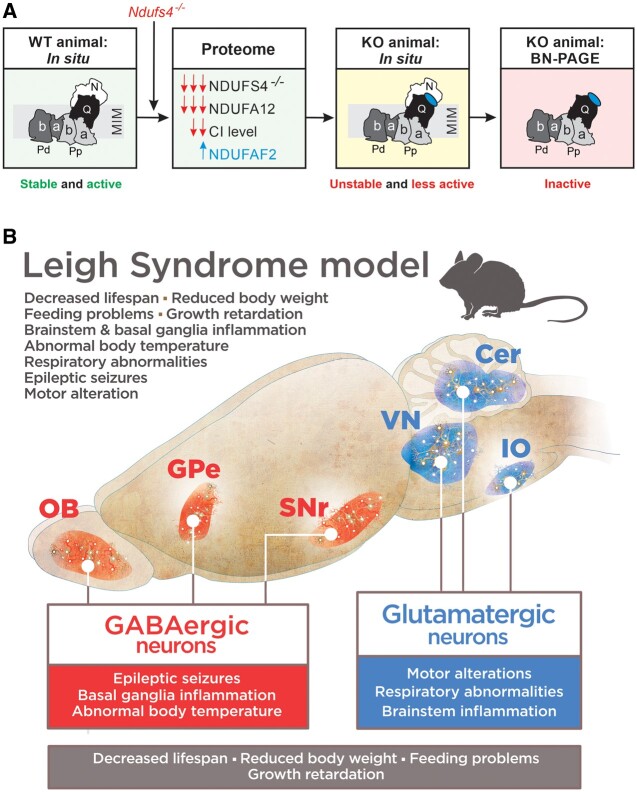
Figure 3.
Consequences of Ndufs4 knockout. (A) Ndufs4 knockout induces absence of the NDUFS4 subunit of CI, near complete absence of the NDUFA12 subunit and increased levels of the CI-attached NDUFAF2 assembly factor. This results in an unstable CI holocomplex that is present at lower levels in situ and therefore displays a lower activity in Ndufs4−/− mice. On isolation, the unstable CI complex loses its N-module, resulting in an inactive ∼800 kDa subcomplex on BN–PAGE gels. Adapted from Adjobo-Hermans et al.64 (B) Genetic dissection of clinical signs in Ndufs4−/−-WB mice. Vglut2-expressing glutamatergic neurons mediate most of the phenotype of Ndufs4−/−-WB mice, such as motor and respiratory alterations, while GABAergic neurons are involved in basal ganglia inflammation, development of epilepsy and hypothermia. Conditional alteration in either population leads to reduced lifespan and decreased body weight. Cer = cerebellum; GPe = external globus pallidus; IO = inferior olive; KO = knockout; OB = olfactory bulb; SNr = substantia nigra pars reticulata; VN = vestibular nuclei; WT = wild-type. Adapted from Bolea et al.82