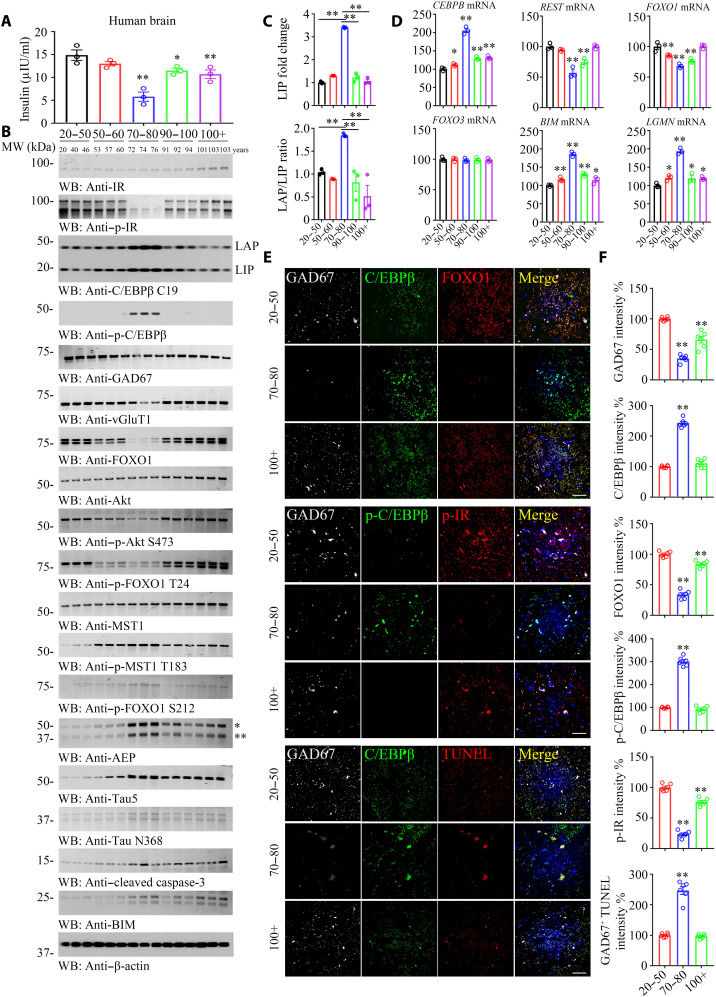
Fig. 6. C/EBPβ mediates insulin signaling in neurons, modulating FOXO1 expression in human brains, related to figs. S10 to S13.
(A) Brain insulin concentration decreased along with aging. Brain tissues from different age groups are detected by human insulin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. (B to D) p-C/EBPβ and p-IR are inversely coupled in the human brains from 70 to 80 years of age group. C/EBPβ and p-C/EBPβ/AEP displayed a parabolic curve during aging while reduced in long-lived individuals. A series of human cerebral cortex frozen tissues of different ages were used for WB detection with various indicated antibodies (B) and real-time PCR (D). Data are represented as means ± SEM; n = 3 per group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the 20 to 50 group; two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. The LAP/LIP isoform ratios were calculated from quantification by immunoblots of (B) (C). Data are represented as means ± SEM; n = 3 per group. **P < 0.01; two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (E) IF costaining on human brain sections. Colocalization of C/EBPβ, FOXO1, p-C/EBPβ, p-IR, and TUNEL in GAD67+ neurons from different ages’ human cerebral cortexes. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy was performed in human cerebral cortex. Scale bars, 40 μm. The image shown is representative of immunofluorescence labeling performed in three individuals. (F) Quantification of (E). Data are represented as means ± SEM; n = 6 per group. **P < 0.01 versus the 20 to 50 group; Mann-Whitney U test with multiple testing correction by Holm’s method.