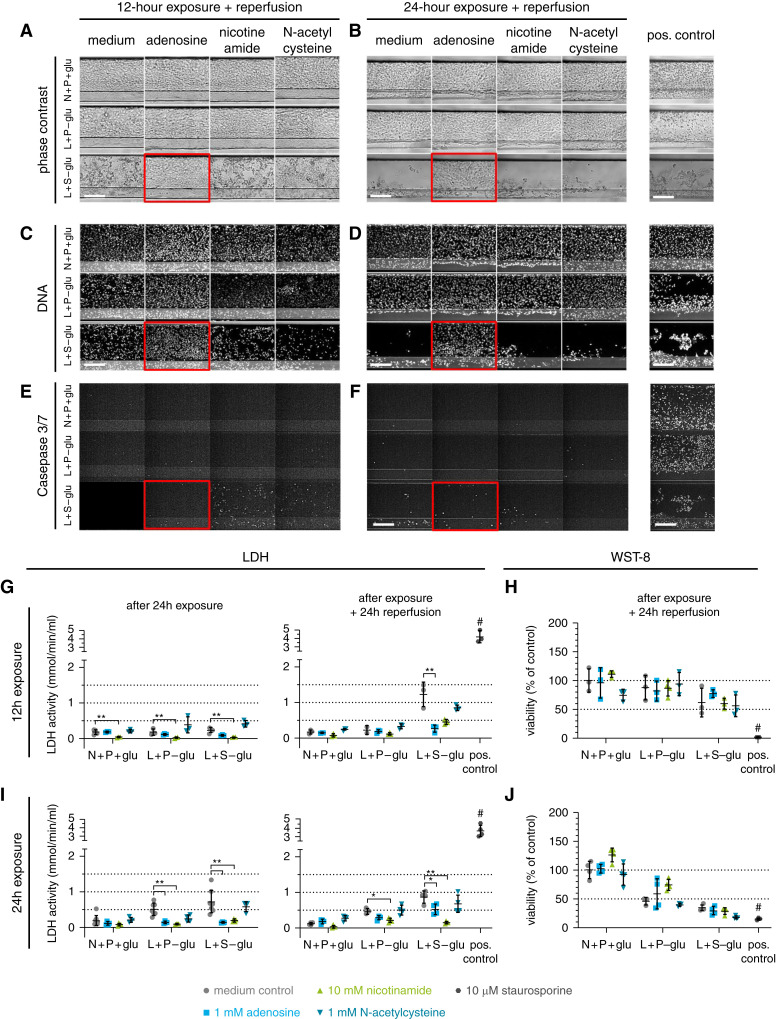
Figure 5.
Coincubation with adenosine decreases ischemia-induced AKI. Cultures were exposed to the selected ischemic conditions L+P-glu and L+S-glu for either 12 or 24 hours, followed by a 24-hour reperfusion, in the presence of adenosine, nicotinamide, or N-acetylcysteine. N+P+glu medium only is the normoxic control condition. (A–F) Images of a region of the RPTEC tubule (see Figure 4B) after 12-hour exposure and reperfusion (A, C, and E) or after 24-hour exposure and reperfusion (B, D, and F). Red squares indicate a protective effect of adenosine compared with the medium control of the same ischemic condition in phase-contrast imaging (A and B), DNA staining (C and D), and caspase-3/7 staining (E and F). Scale bar, 200 µm. (G and I) LDH activity and (H and J) WST-8 viability relative to the N+P+glu medium control after exposure to the ischemic condition for 12 hours (G and H) or 24 hours (I and J) followed by reperfusion for 24 hours for both conditions. One-way ANOVA compares the coincubations with the medium control of the same ischemic condition. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. #, positive control differs significantly with all medium controls (P<0.01). Error bars represent the standard deviation. Staurosporine (10 µM) was included as a positive control. n=3–8 chips per condition. Both experiments (12- and 24-hour exposure) were repeated (Supplemental Figure 2).