Extended Data Fig. 5: ATP5B-L394F mutation has opposing effects on apoptolidin and ammocidin sensitivity.
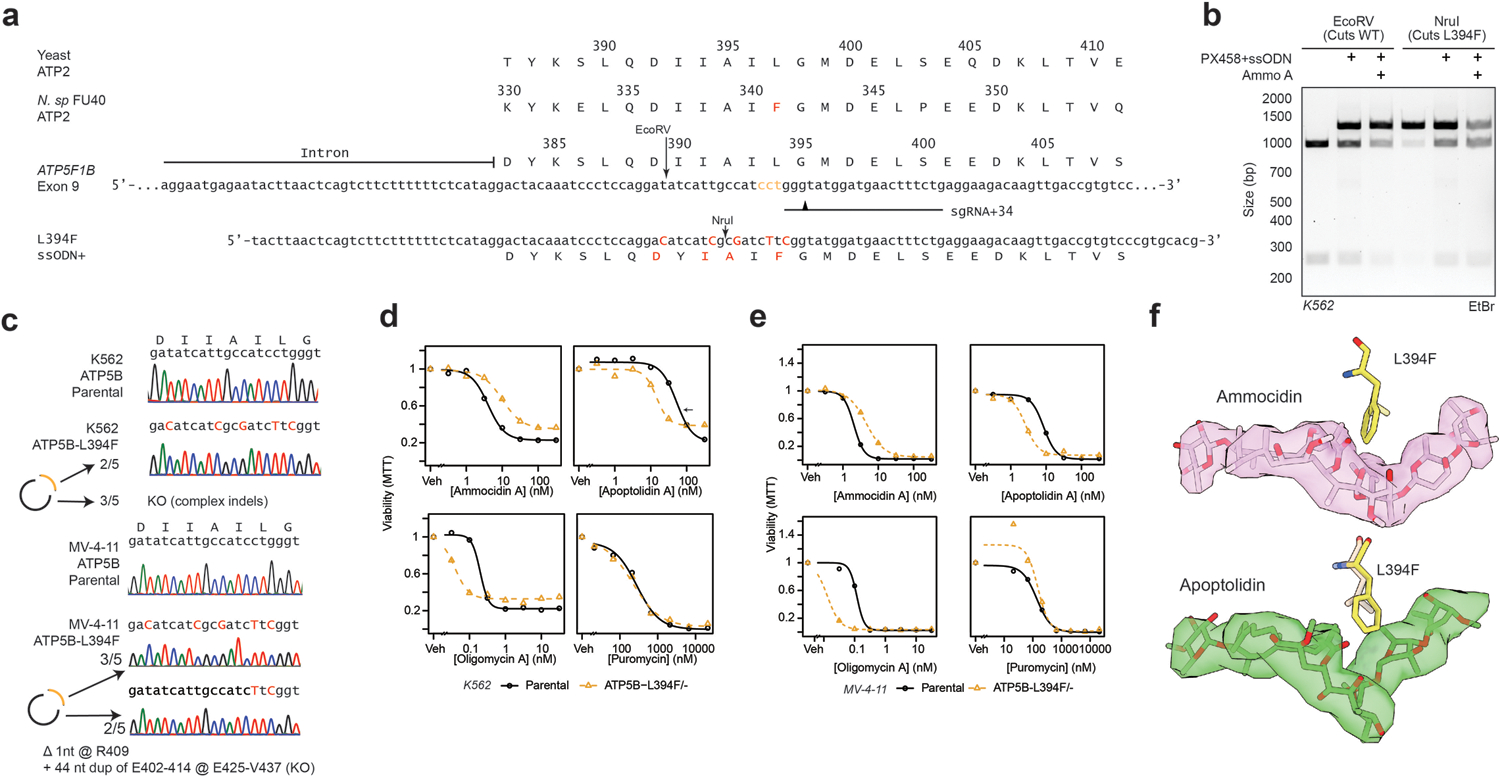
a, Multiple sequence alignment of ATP synthase β subunit C-terminal domain and CRISPR/Cas9 HDR editing strategy for human exon 9 and using plasmid (PX458) encoding sgRNA and Cas9 and ssODN repair template, PAM sites labeled in yellow, cut locations noted with arrowhead, edits noted in red, restriction sites noted; b, Restriction digest of ATP5F1B Exon 9/10 amplicons from parental K562s or PX458 + ssODN treated K562s treated with Ammo A (150 nM x 5 d) showing loss of wildtype allele and retention of edited alleles with ammocidin treatment; c, Confirmation of introduction of ATP5B-L394F mutation and KO of wildtype ATP5B in K562s and MV-4–11 cells by Sanger sequencing; d, ATP5B-L394F sensitizes cells to Apop A and provides some resistance against ammocidin in K562 and e, MV-4–11 cells as measured by MTT assay at 72 h; f, Modeling of the L394 (yeast L397) mutation on the ammocidin (top) and apoptolidin (bottom) structures showing proximity to the hemiketal.
