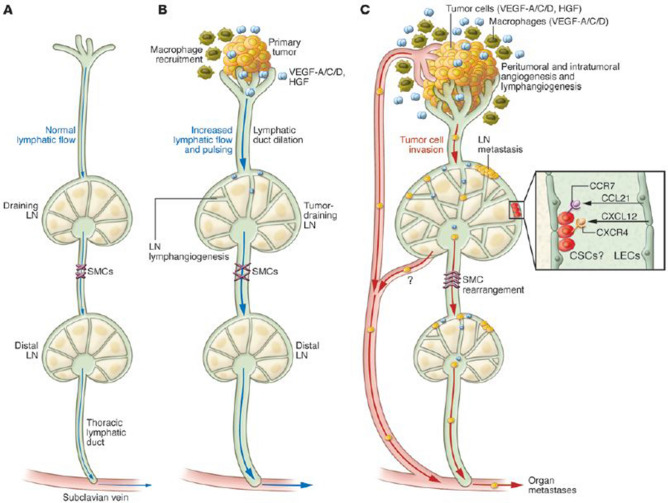
Fig. 6.
An important contribution of tumor and LN lymphangiogenesis to cancer metastasis. A Normal lymphatic tissue drainage through lymphatic capillaries, collecting lymphatics, and LNs. B lymphangiogenic factors produced by premetastatic tumors, including VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGF-A, and HGF, are taken up by peritumoral lymphatic capillaries and are transported via the collecting lymphatics toward the tumor-draining SLN, where they act directly on preexisting lymphatic vessels to induce LN lymphangiogenesis. Tumor-draining lymphatic vessels display an enlarged size and increased lymph flow and pulsing. (C) Once metastatic tumor cells have spread to their draining LNs, they serve as a major
source of lymphangiogenic factors. These promote the remodeling and SMC rearrangement of distant (post-SLN) lymphatic vessels and lymphangiogenesis in distant LNs and promote secondary metastasis, including organ metastasis, via the thoracic duct, which connects to the venous circulation via the subclavian vein. CSC, cancer stem cell. The chemokines CCL21 and CXCL12, released by activated lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) within SLNs, might provide a niche for cancer cells with stem cell–like properties that express the receptors CCR7 and CXCR4 [57]. Permission has been obtained to reproduce legend and figure for Fig. 6 from Journal of Clinical Investigation [57]