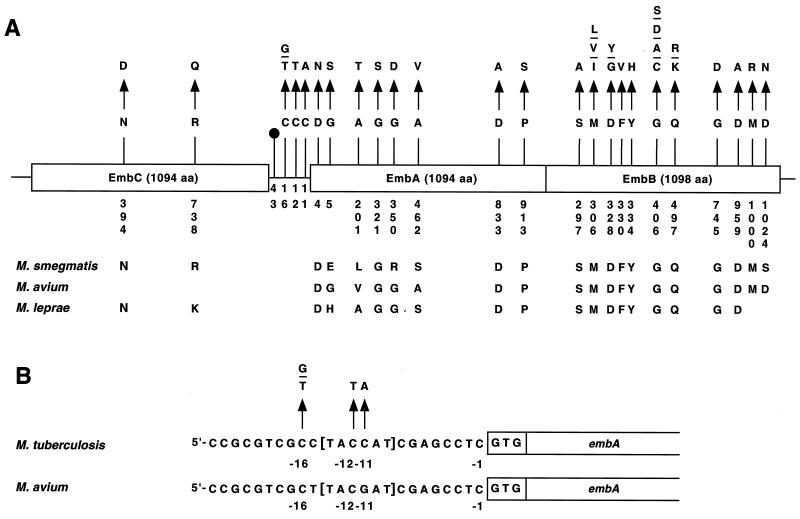
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of EMB resistance-related polymorphisms in the embCAB genes. (A) Overview of the mutations identified. Variant amino acid residues and nucleotides are numbered vertically. The corresponding amino acid residues found in M. smegmatis, M. avium, and M. leprae are shown. The symbol at position −43 denotes a dinucleotide deletion of a guanine and a cytosine. (B) Expanded view of the embC-embA intergenic region. The nucleotide substitutions identified in the region containing a putative TATA box (marked in brackets) are shown. The single-letter amino acid (aa) abbreviations are used. A, alanine; C, cysteine; D, aspartic acid; E, glutamic acid; F, phenylalanine; G, glycine; H, histidine; I, isoleucine; K, lysine; L, leucine; M, methionine; N, asparagine; P, proline; Q, glutamine; R, arginine; S, serine; T, threonine; V, valine; Y, tyrosine.