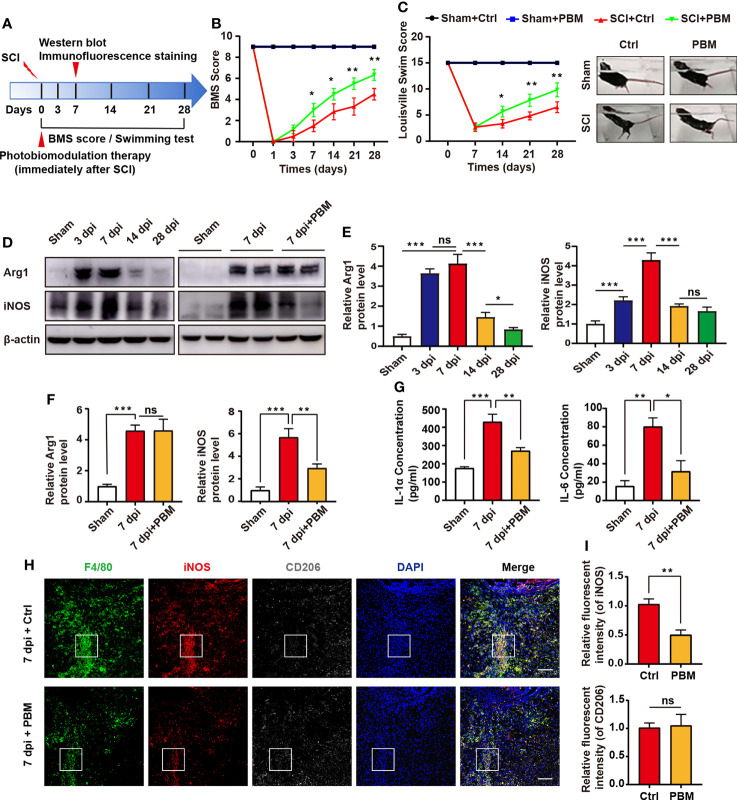
Figure 1.
PBM promotes the recovery of motor function in mice with compressive SCI and reduces the neurotoxic polarization of macrophages in the injury area. (A) Experimental paradigm. (B) Statistical analysis of the Basso Mouse Scale (BMS) score in the sham surgery and SCI groups over a period of 28 days (n = 6 mice per group at each time point). (C) Photographs of varying degrees of trunk instability observed after SCI or sham surgery and statistical analysis of the Louisville Swimming Scale (LSS) over 28 days in the control and PBM groups (n = 6 mice per group at each time point). (D–F) Immunoblotting of Arg1 (M2 macrophage marker) and iNOS (M1 macrophage marker) at 3 dpi, 7 dpi, 14 dpi, and 28 dpi or after sham surgery (28 days after the sham operation) (n = 3 mice per group at each time point). (G) ELISA results for IL-1α and IL-6 in the injured spinal cords of each group at 7 dpi. (H, I) Representative immunohistochemical staining of F4/80 (macrophage marker), iNOS (M1 macrophage marker) and CD206 (M2 macrophage marker) in the epicentre of the injured spinal cord of the control and PBM groups at 7 dpi (scale bar = 100 μm). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.