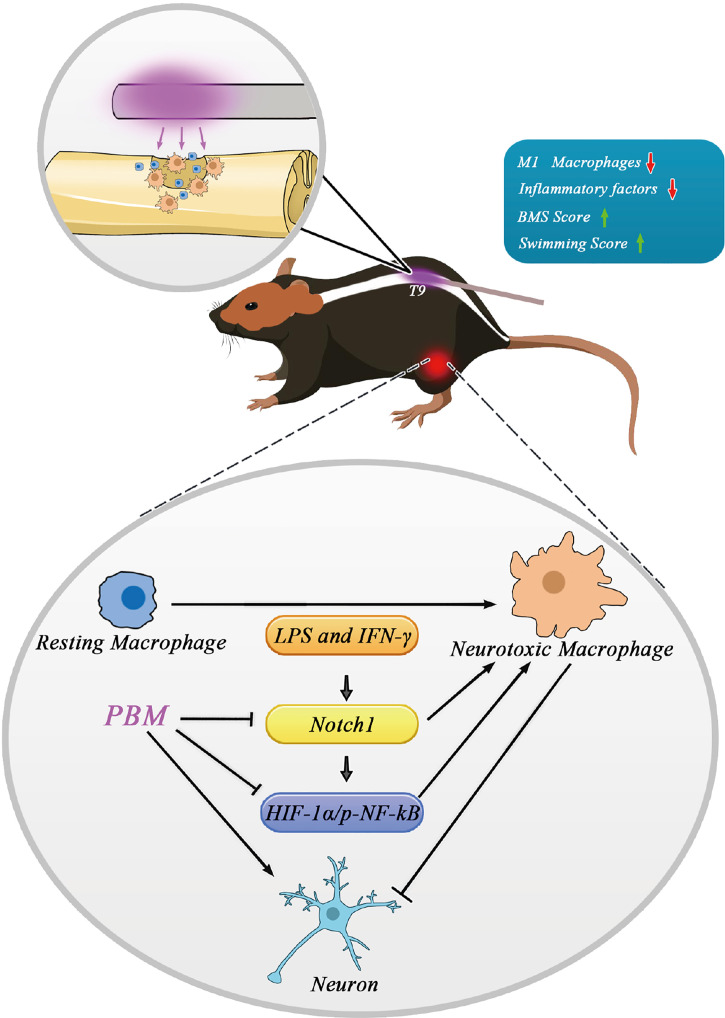
Figure 8.
Schematic model showing the regulatory role of PBM on M1 macrophages and its possible molecular mechanisms. Macrophages in the resting state become activated and are involved in neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury. Activated neurotoxic macrophages have damaging effects on neurons by secreting cytotoxic cytokines. The Notch1 and HIF-1α/p-NF-κB axis are involved in macrophage activation. Specifically, the Notch1 pathway is involved in the activation of neurotoxic macrophages and the expression of HIF-1α and p-NF-κB. The neuroprotective mechanism of PBM may be related to its inhibition of the Notch1-HIF-1α/p-NF-κB axis, which is associated with the activation of neurotoxic macrophage cells.