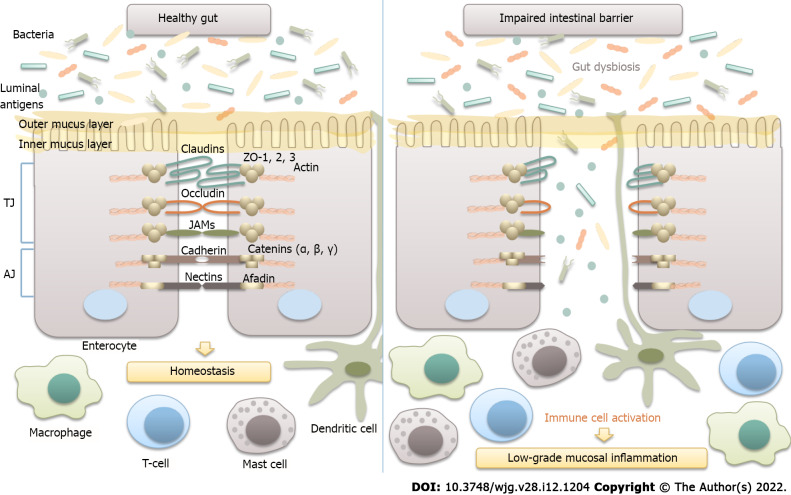
Figure 2.
Microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity. The intestinal barrier plays an essential role in maintaining host homeostasis. It is mainly composed of the mucus layer, the epithelial layer, and the underlying lamina propria. Intestinal epithelial cells are tightly attached to each other by junctional complexes. Tight junctions (TJs) are composed of several proteins, including occludin, claudins, zonula occludens (ZOs), and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs), which interact with each other, as well as with the cytoskeleton. The adherence junction is composed of the nectin-afadin system and the E-cadherin-catenin system. Intestinal epithelial barrier integrity prevents the translocation of bacteria and luminal antigens to the mucosa, thus averting their interaction with the host immune system and the development of low-grade mucosal inflammation in the gut wall. TJ: Tight junctions; AJ: Adherence junction; JAM: Junctional adhesion molecules.