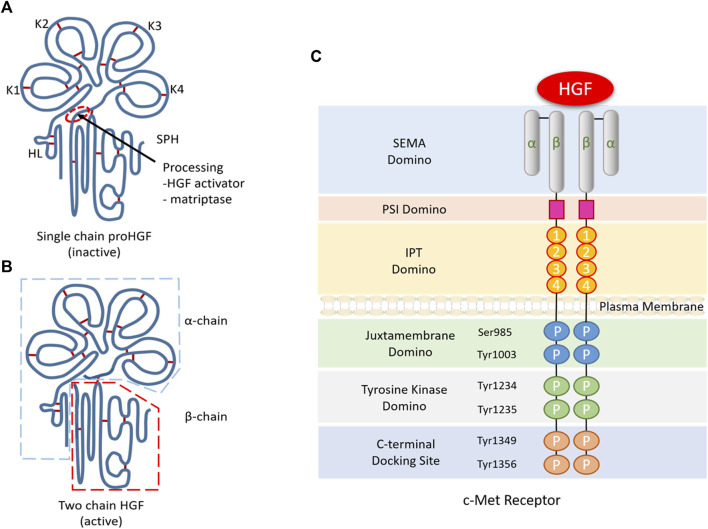
FIGURE 1.
Structure and molecular signalling components of HGF/c-Met. (A). The α-chain of HGF is composed of an N-terminal hairpin loop (HL) attached four kringle domains (K1-K4), and the β-chain is composed of a serine protease homology domain (SPH) lacking proteolytic activity. (B). Active HGF is a heterodimeric molecule composed of an α-chain and a β-chain. (C). C-Met consists of a small α-chain and a larger β-chain, including extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains. The extracellular domain contains a large semaphore protein (SEMA) domain where HGF binds to c-Met. After the SEMA domain, a plexin, semaphorin and integrin-rich (PSI) domain and four immunoglobulin/plexin/transcriptional factors (IPT) domains make up the rest of the extracellular domains. Intracellularly, the C-terminal tail of c-Met β-chain containing two phosphorylation sites (Ser985 and Tyr1003), two tyrosine residues (Tyr1234 and Tyr1235) and a multisubstrate docking site (Tyr1349 and Tyr1356).