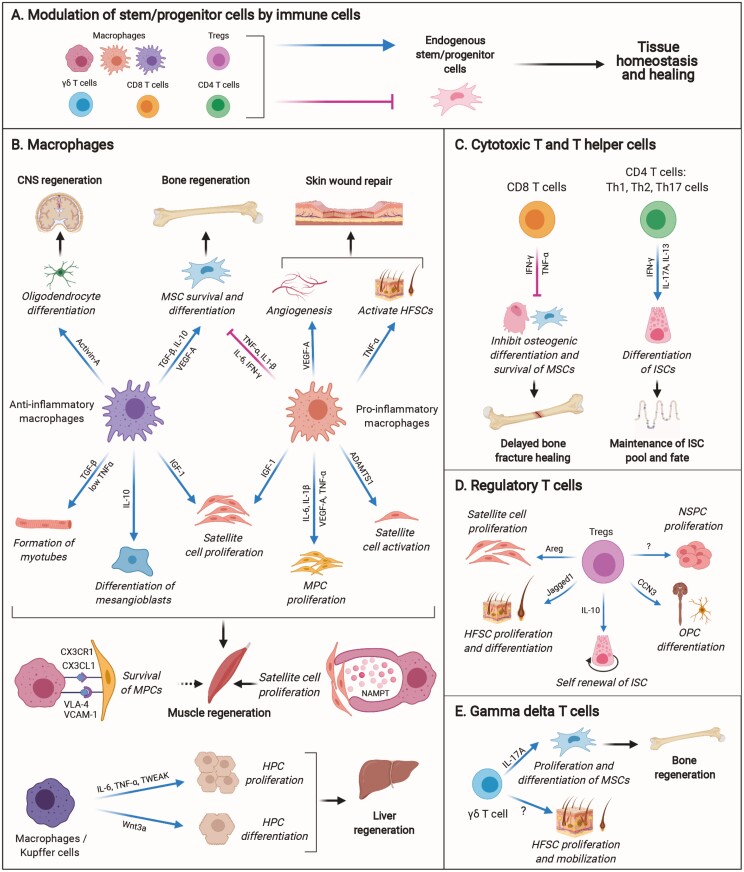
Figure 1.
Modulatory effect of immune cells on endogenous stem/progenitor cells. (A) Macrophages and T cells have direct positive or negative effects on endogenous stem/progenitor cells in tissue homeostasis and healing. (B-E) Example of immune cells and their derived factors that exert positive or negative effects on stem/progenitor cells in tissue homeostasis, repair and regeneration. Abbreviations: CNS, central nervous system; FAPs, fibro-adipogenic progenitors; HFSCs, hair follicle stem cells; HPCs, hepatic progenitor cells; HSPCs, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; ISCs, intestinal stem cells; MPCs, myogenic precursor cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NSPCs, neural stem and progenitor cells; OPCs, oligodendrocyte progenitor cells.