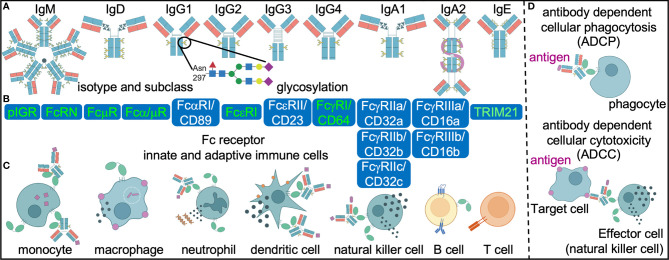
Figure 2.
Differential antibody engagement with Fc receptors mediate diverse innate and adaptive immune cell effector functions. Antibody diversity (A) in antigen specificity (theoretical n=1013), isotype (n=5), subclass (n=6) and post-translational glycosylation (theoretical n=36 possible different moieties) influence engagement of Fc receptors. Subsequent differential activation of high (red) and low (white) affinity Fc receptors (B) expressed on innate and adaptive immune cells (C) have the potential to mediate effector functions such as antibody dependent cellular phagocytosis and cytotoxicity (D) that in concert determine the heterogenous outcomes in human TB.