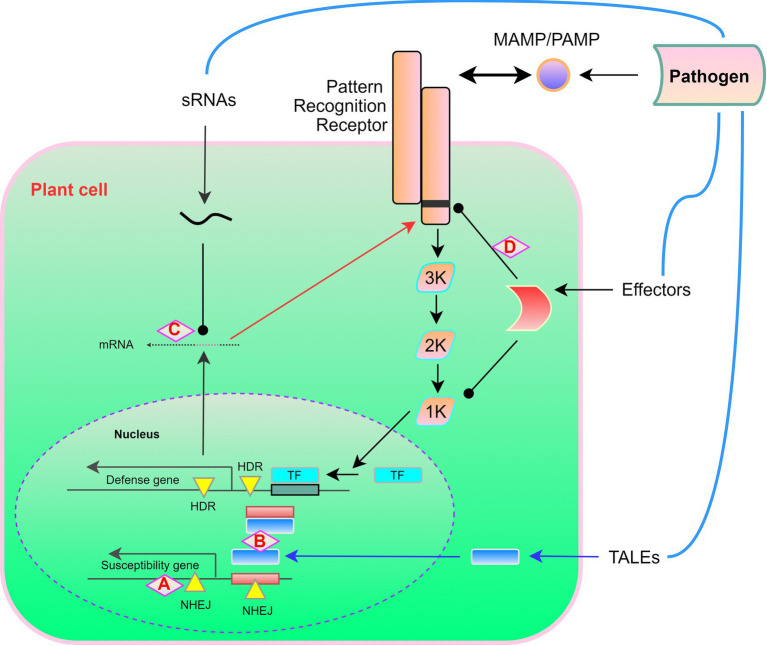
Figure 3.
A potential target for applying CRISPR-Cas for engineering of “non-transgenic” disease resistance in plants. In response to pathogen recognition, the plant-induced defense response involves a MAP kinase phosphorylation cascade, which leads to the activation of transcription factors and the expression of defense-related genes. (A) Open reading frame disruption by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) causes frameshift mutations in susceptibility genes. (B) NHEJ eliminates cis elements to prevent transcription activator-like effector (TALE) activation of susceptibility genes and homology-directed repair (HDR) introduces cis elements, which promotes the TALE-triggered activation of defense genes. (C) Rewriting of transboundary RNAi via HDR-mediated pathogen siRNA targeting. (D) HDR-mediated coding sequence rewriting replaces the effectors produced by pathogens for amino acid residues required for protein recognition, thereby preventing, for example, cleavage or modification. The figures are adopted with modification from those presented by Schenke and Cai (2020).