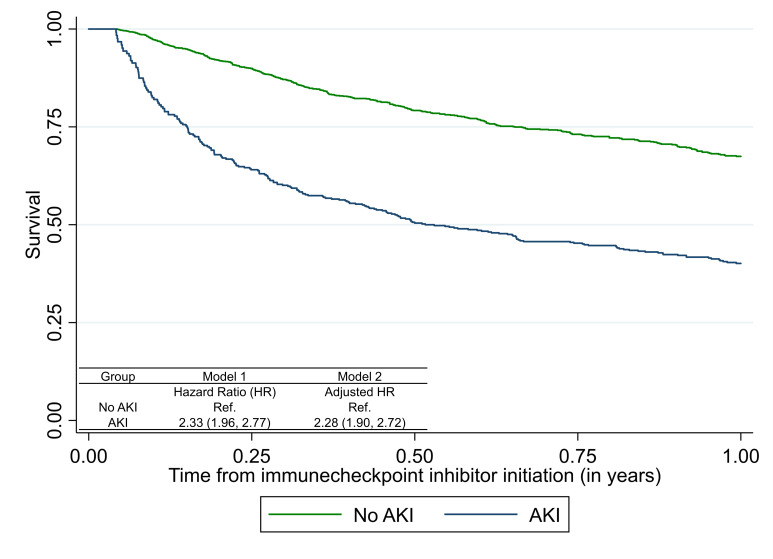
Figure 2.
Association of acute kidney injury (AKI) with mortality after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Association of AKI with mortality in all participants initiated on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy using time-varying Cox proportional hazards models where exposure (AKI) was treated as a time-varying covariate updated once if it occurred and patient considered as exposed for the remainder of the analysis period. Follow-up starts 15 days after initiation of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for both analyses. Model 1 tests univariable association of AKI with mortality; model 2 controls for age, sex, race, ethnicity, presence of comorbidities (CKD, CHF, COPD, cirrhosis, diabetes, Elixhauser Comorbidity Score), cancer type (lung, melanoma, other), metastasis, baseline creatinine, and time-updated administration of ICI. Extended Kaplan-Meier curve accounting for time-varying covariate. Mortality rate (per 1000 person-years): no AKI, 445 (404, 489); AKI, 905 (786, 1042); overall, 529 (489, 572). CHF, congestive heart failure; CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.