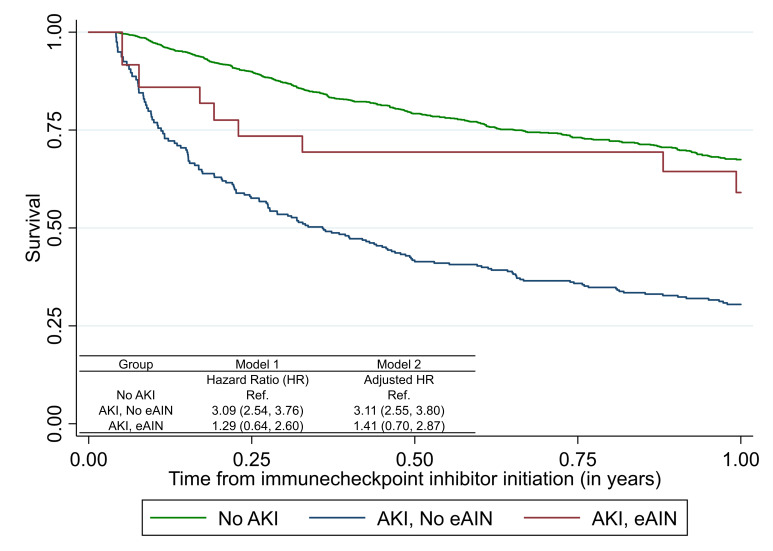
Figure 3.
Association of acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) with mortality after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. estimated AIN (eAIN) defined as those in the top 10% of AIN probability as determined by the diagnostic model. Model 1 tests univariable association of AKI or eAIN with mortality; model 2 controls for age, sex, race, ethnicity, presence of comorbidities (CKD, CHF, COPD, cirrhosis, diabetes, Elixhauser Comorbidity Score), cancer type (lung, melanoma, other), metastasis, and time-updated administration of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI). Association of estimated AIN with mortality in all participants initiated on ICI therapy using time-varying Cox proportional hazards models where exposure (presence or absence of AKI or eAIN) was treated as a time-varying covariate updated once if it occurred and patient considered as exposed for the remainder of the analysis period. Extended Kaplan-Meier curve accounting for time-varying covariate. Follow-up starts at 15 days after initiation of ICI therapy. Mortality rates (per 1000 person-years): no AKI, 498 (452,547); AKI without eAIN, 1487 (1250,1770); AKI with eAIN, 617 (308,1233). CHF, congestive heart failure; CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.