Fig. 2 |. RNA modifications affect the RNA’s secondary structures and interaction with immune sensors.
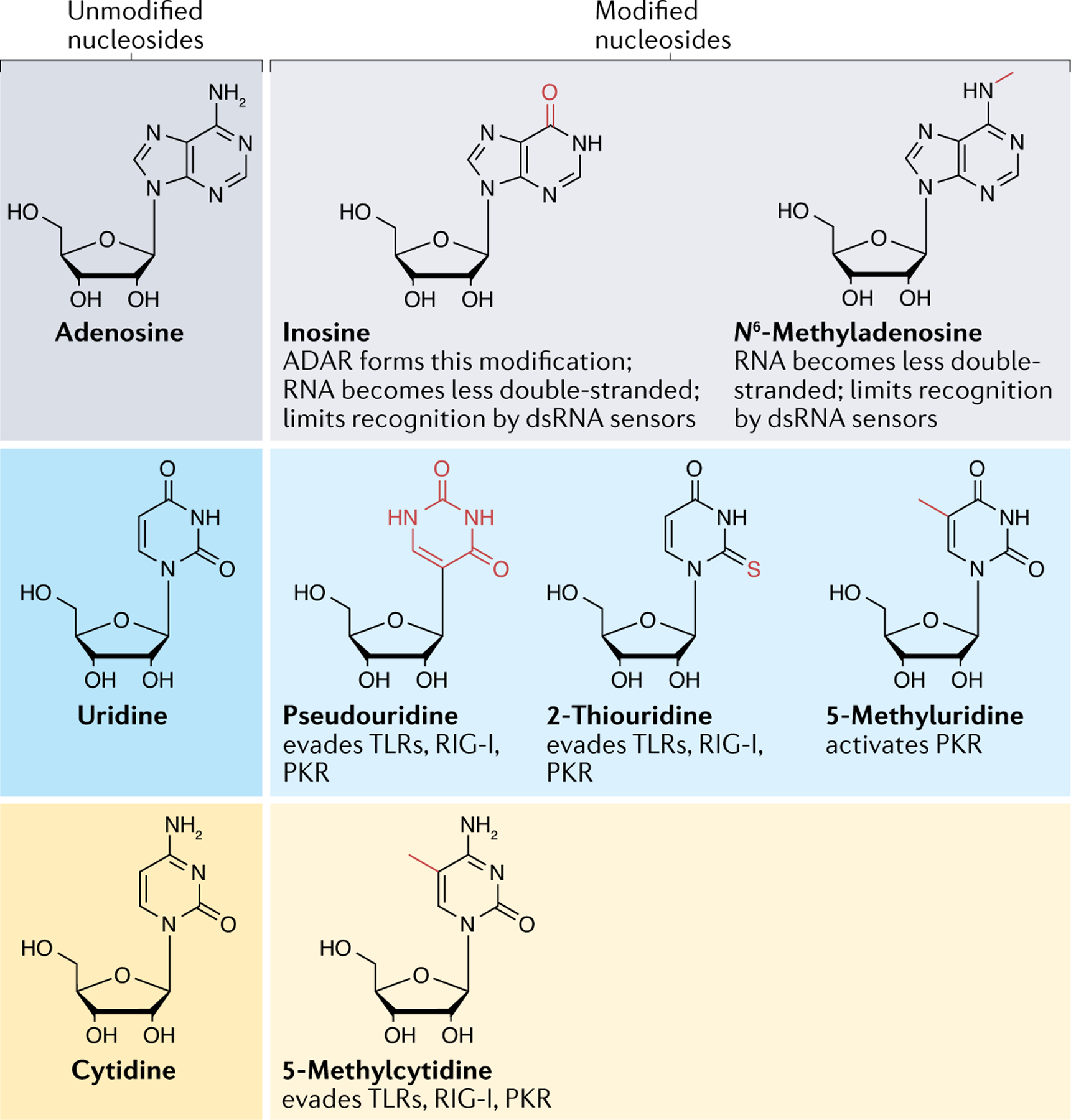
The canonical nucleosides adenosine, uridine and cytidine can be modified by enzymes that install new chemical groups (shown in red). The RNA modifications can change base-pairing interactions, protein binding and secondary structures, which can prevent the modified RNAs from forming immunogenic structures, such as double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs), and evading detection by immune sensors, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs), RIG-I and protein kinase R (PKR). ADAR, double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase.
