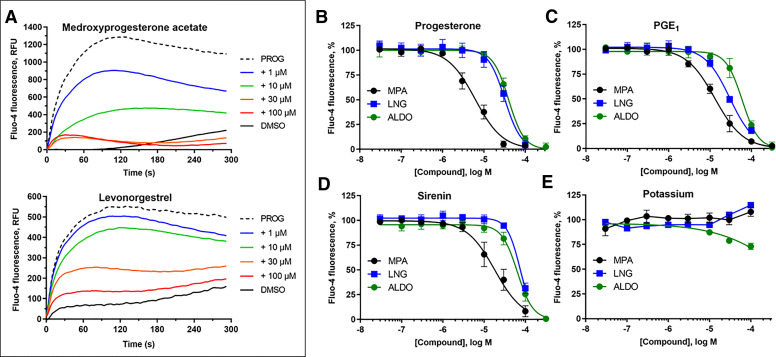
Fig. 7.
The steroids MPA, LNG, and ALDO inhibit PROG-, PGE1-, and l-sirenin-induced calcium influx in human sperm. (A) Representative FLIPR traces showing concentration-dependent reduction of PROG-mediated increase in [Ca2+]i by MPA (upper) and LNG (lower). FLIPR traces for inhibition of PGE1- and l-sirenin-induced calcium influx by MPA and LNG are in Supplemental Figs. 7 and 8, respectively, and traces for ALDO antagonism of all three activators are in Supplemental Fig. 9. (B–E) Potencies of MPA, LNG, or ALDO for inhibiting (B) PROG-, (C) PGE1-, (D) l-sirenin-, or (E) high K+/high pH-induced calcium influx. Ligand-induced activation used EC80 concentrations of activator (30 nM PROG, 10 nM PGE1, 3 µM l-sirenin). Buffer containing 140 mM K+, pH 8.2 was added to elicit alkalinization/depolarization calcium influx (E). The data in B–E are plotted as the mean ±SEM and expressed as a percent of the response produced by each activator alone. IC50 and n values are in Table 4.