Fig. 4.
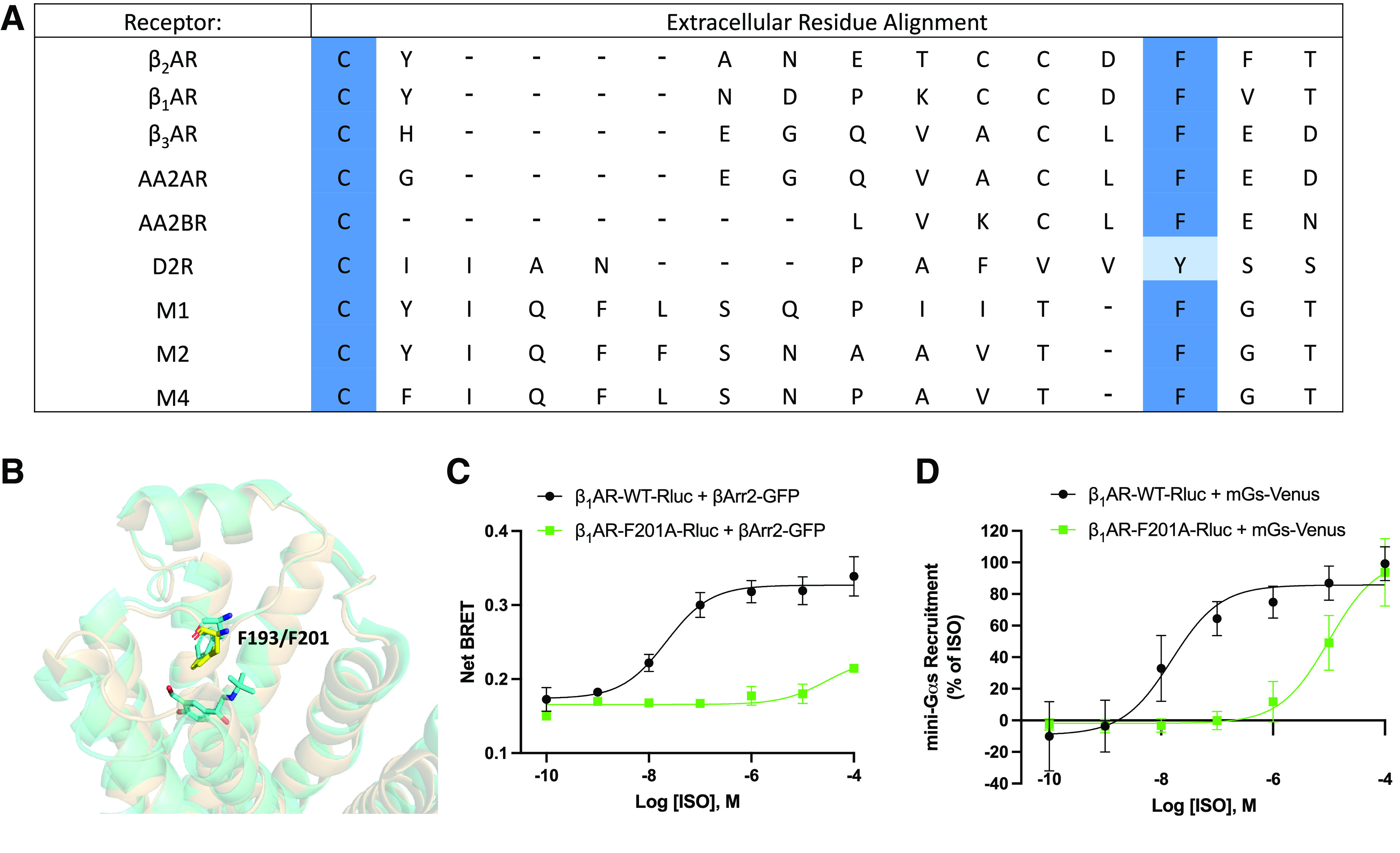
Analysis of extracellular residues of class A G protein-coupled receptors. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of several class A G protein-coupled receptors. βAR=β-adrenergic receptor, AAR=adenosine receptor, DR=dopamine receptor, MR=muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. (B) Structural alignment of β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR, tan) and β1-adrenergic receptor (β1AR, yellow, PDB: 7BTS). β2AR residue F193 and β1AR residue F201 are indicated by sticks. (C) β-arrestin recruitment to wild-type β1AR (β1AR-WT) and β1AR-F201A as measured by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Human embryonic kidney 293cells co-transfected with β-arrestin2-GFP10 and indicated β1AR-WT-RlucII or β1AR-F201A-RlucII constructs were incubated with coelenterazine 400a for 2 minutes and then stimulated with indicated concentrations of isoproterenol (ISO). Data were collected at 6 minutes post agonist addition. n = 3 independent experiments. (E) Dose response curves for ISO promoted mini-Gs recruitment to β1AR by BRET. Human embryonic kidney 293cells transiently transfected wild-type or mutated β1AR-Rluc and NES-Venus-mGs were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of ISO for 15 minutes and BRET signal was measured. n = 3 independent experiments.
