Figure 1. Overview of ST Technologies.
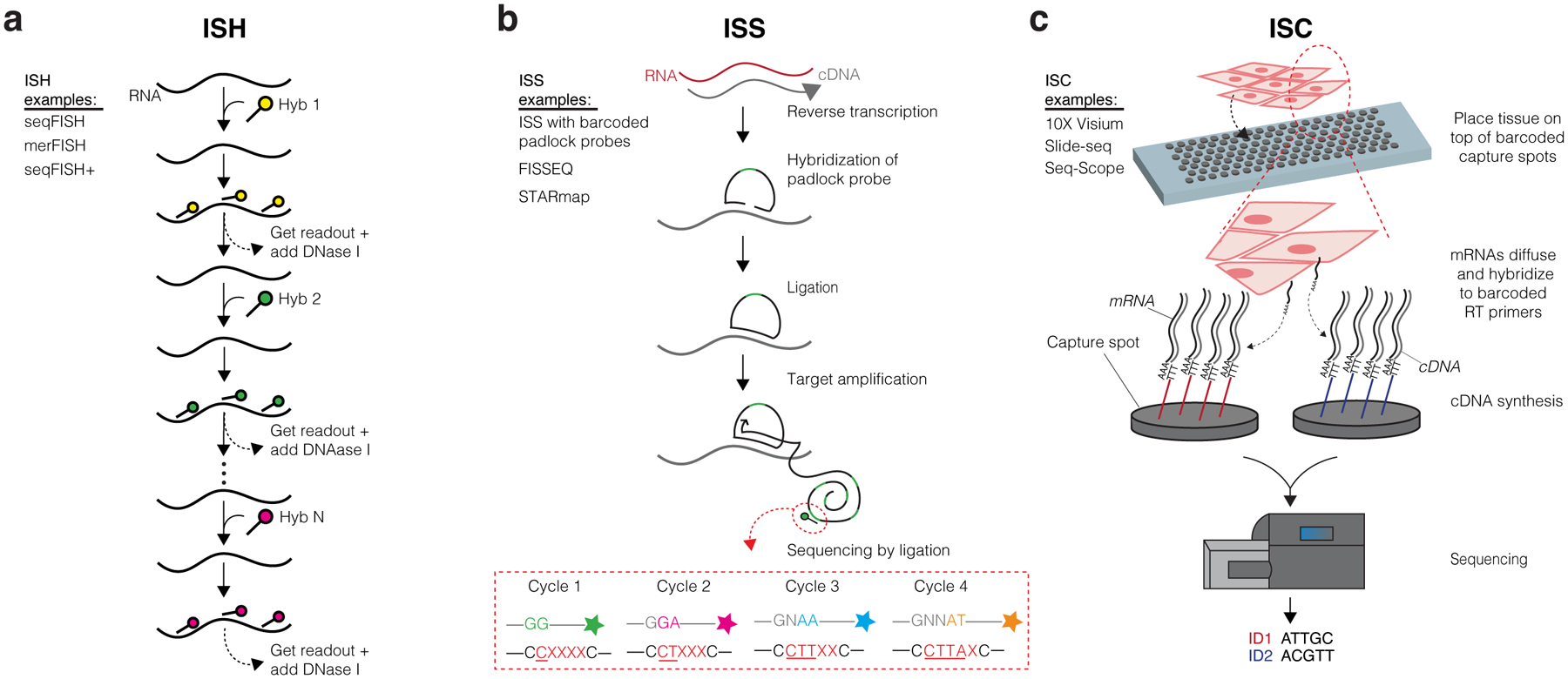
(a) In situ hybridization (ISH) methods detect specific target genes via use of fluorophore-labeled probes. Signals from probes targeting short sequences of transcripts are propagated by consecutive rounds of hybridization, imaging, and probe stripping. The steps depicted specifically follow seqFISH methods. (b) In situ sequencing (ISS) methods typically involve the hybridization and ligation of a barcoded padlock probe complementary to the RNA or cDNA of a target gene. Multiple rounds of target amplification and sequencing by ligation then allow for spatial resolution of the distinct target gene. The steps depicted specifically follow the ISS with barcoded padlock probes method. (c) In situ capturing (ISC) methods use capture spots containing an array of RT primers with distinct positional barcodes and poly-T sequences to capture mRNA transcripts. Reverse transcription produces cDNAs that are extracted and sequenced using next generation sequencing. Positional barcodes are mapped to specific locations on the tissue and enable spatial visualization of the transcriptome. The steps depicted specifically follow 10X Visium methods.
