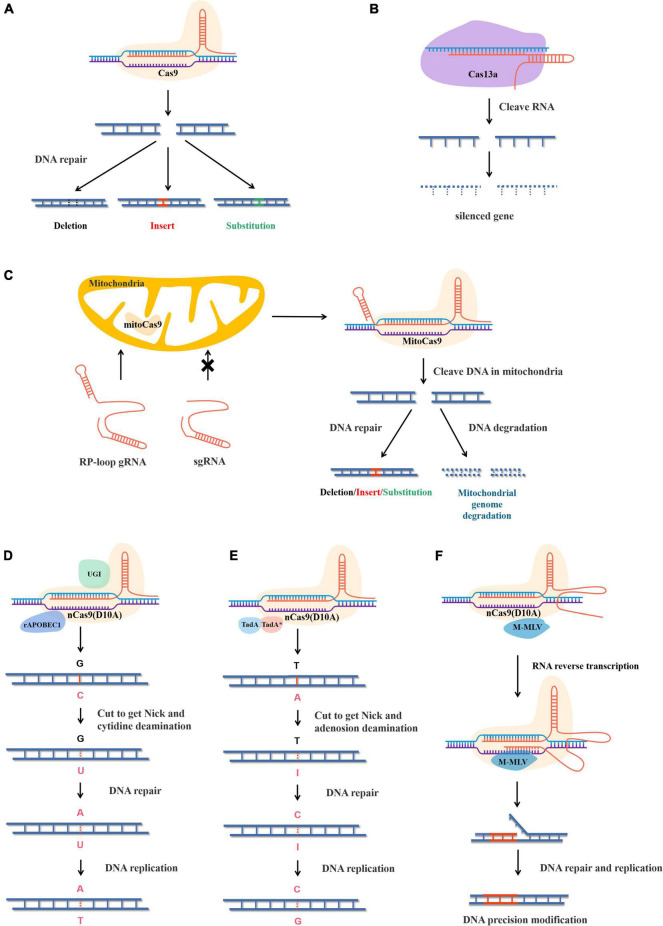
FIGURE 1.
Structure and principle of different gene editing systems. (A) CRISPR-Cas9 cleave double-stranded DNA and causes DSB and the genes are edited under the action of the plant’s own DNA repair mechanism. (B) Rp-loop structure promotes sgRNA entering the mitochondrial and CRISPR-MitoCas9 result mitochondrial gene editing or genome degradation. (C) CRISPR-Cas13a cleaves ssRNA and causes ssRNA degradation. (D) The CBEs replaces bases with cytosine deaminase and T-A replace C-G under the action of plant DNA repair. rAPOBEC1, rat cytidine deaminase; GUI, uracil glycosylase inhibitor. (E) The adenine base editor replaces bases by adenine deaminase and G-C replace A-T under the action of plant DNA repair. TadA, wild-type Escherichia coli tRNA adenosine deaminase. TadA*, mutant TadA. (F) nCas9(D10A) cleaves single strands of DNA to form Nick, and pegRNA acts as a template to replace the sequence under the action of reverse transcriptase. Precise modification of target sequences by plant DNA repair. M-MLV, Moloney mouse leukemia virus reverse transcriptase.