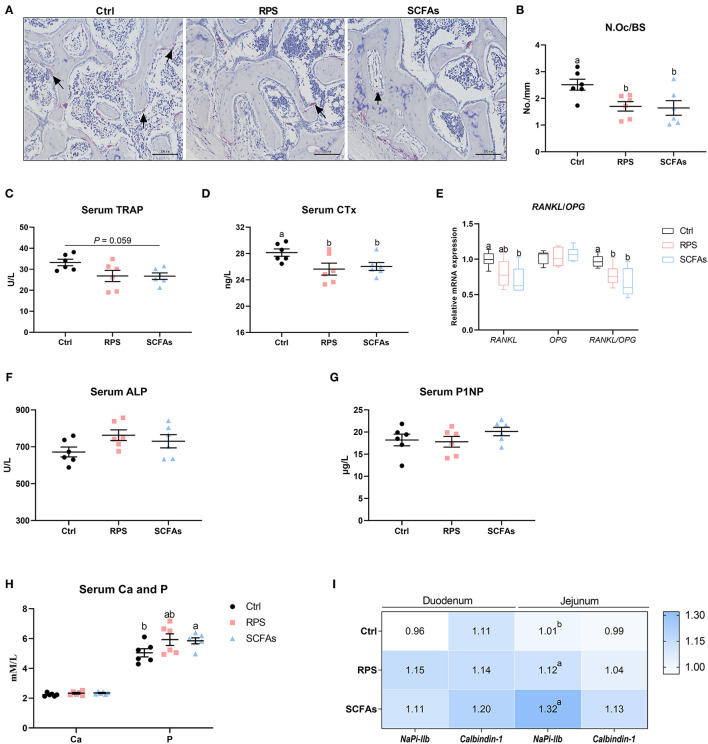
Figure 3.
Dietary RPS and drinking SCFAs administration suppressed osteoclastic bone resorption and induced phosphorus (P) absorption in meat ducks. (A) Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining of tibial sections. Bar = 100 μm. (B) The number of osteoclast (N.Oc/BS) in proximal tibias was determined by histomorphometry. Circulating (C) TRAP activity and (D) C-terminal cross-linked telopeptide of type I collagen (CTx) concentrations. (E) Real-time (RT)-PCR analysis for mRNA expression of receptor activator for nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprogerin (OPG) in the proximal end, and the ratio of RANKL/OPG was calculated. Serum bone formation including (F) procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) and (G) alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level, as well as (H) serum calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) concentration were evaluated. (I) The mRNA abundance of RT-PCR analysis for mRNA expression of sodium-dependent phosphorus transport protein II (NaPi-IIb) and calbindin-1 in duodenum and ileum. Data are expressed as mean and SD. a,b Mean values with different letters are significantly different by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post-hoc test (p < 0.05).