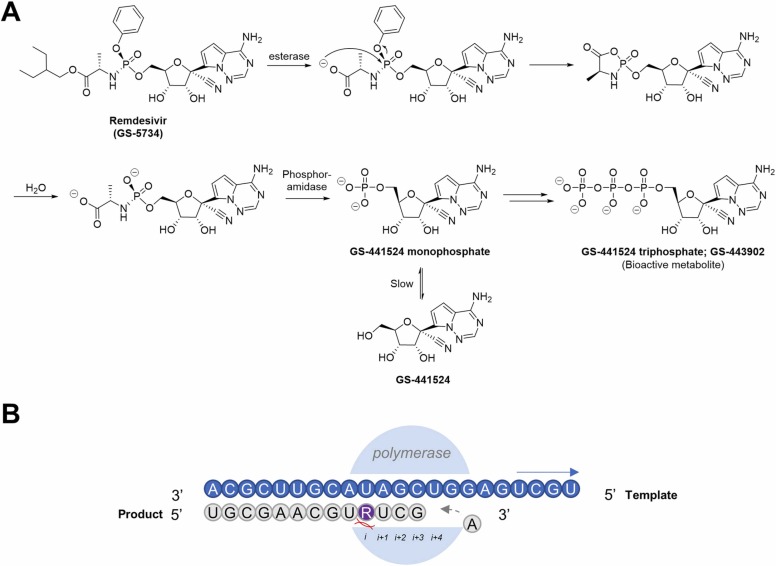
Fig. 3.
(A) Metabolism of prodrug remdesivir (GS-5734) to GS-441524 monophosphate, which is phosphorylated in host cells to the bioactive triphosphate of GS-441524 (GS-443902). (B) When GS-441524 (represented in purple) is incorporated into the replication strand (represented in grey), the machinery stalls while trying to incorporate the 4th nucleotide due to steric clashes between the 1’-CN group of GS-441524 and the polymerase, resulting in its delayed chain termination mechanism of action.