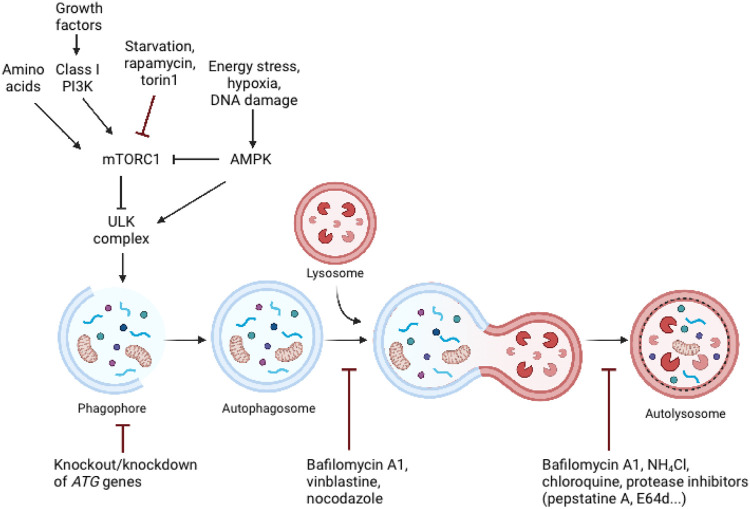
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of major signalling pathways that regulate autophagy and the inhibition of autophagy by genetic and pharmacological approaches. Autophagy is controlled by a variety of growth and nutrition signaling pathways. mTORC1 activity, which reflects cellular nutritional status, is a major regulator of autophagy. Since the ULK complex is inactivated by mTORC1 activity, sufficient amounts of amino acids and growth hormones prevent autophagy. Cellular stress, such as energy deprivation, DNA damage, and hypoxia inhibit mTORC1 activity, resulting in the release and activation of the ULK complex, which triggers autophagosome formation. Adapted from biorender.com.