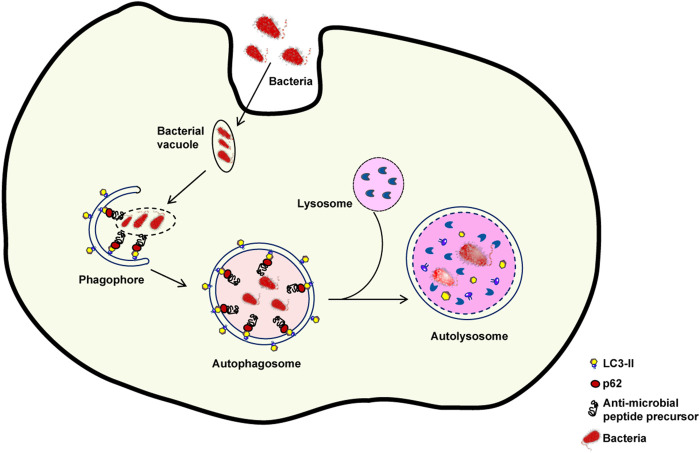
FIGURE 3.
Xenophagy: An intracellular defence mechanism against bacteria. Following host cell invasion, vacuoles harboring intracellular bacteria merge with autophagosomes and engage the autophagy machinery to kill the pathogenes in autolysosomes. However, several bacteria have developed mechanisms to escape xenophagy. For example, some bacteria are able to decrease the fusion of bacteria-containing vacuoles with autophagosomes or of autophagosomes with lysosomes. If the autophagic process is inhibited, bacterial reproduction can occur.