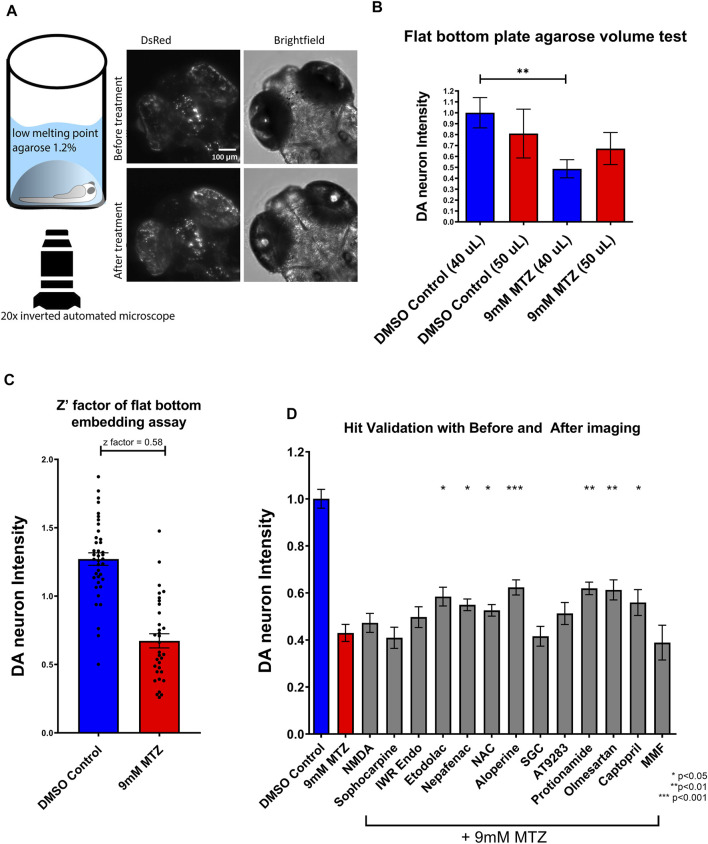
FIGURE 3.
Establishment of a secondary hit validation assay and validation of candidate hit compounds. (A) Schematic of the secondary hit validation assay using agarose embedding and automated imaging. At 5 dpf, larvae were embedded in 1.2% agarose and imaged under brightfield and DsRed channels. The larvae were treated with 0.2% DMSO or 9 mM MTZ with or without hit compounds. At 6 dpf, larvae were again imaged with the same x,y,z coordinates on the microscope. Image shown is an example of a 0.2% DMSO control. (B) Comparison of 40 and 50 μL 1.2% low melting point agarose for embedding. Samples embedded with 40 μL agarose showed significant difference between DMSO control and 9 mM MTZ (n = 8; p < 0.05, unpaired t test), whereas those with 50 μL agarose did not, due to increased distance between the objective and the samples. (C) Evaluation of Z′-factor for the secondary hit validation assay. The 0.2% DMSO control and 24 h of 9 mM MTZ treatment showed a significant difference in DA neuron intensity with a z’factor of 0.58. (D) Secondary hit validation of compounds with the embedding assay. Samples were treated with 10 μM of each candidate compound and 9 mM MTZ for 24 h. Etodolac, nepafenac, NAC, aloperine, Protionamide, olmesartan, and captopril showed significantly greater “BHS After treatment” to “BHS before treatment” ratio compared to the negative control (9 mM MTZ) (n = 22 to 30; one-way ANOVA F = 12.33, p = 0.003, post-hoc Fishers LSD *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). MTZ: metronidazole, DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide, NAC: N-Acetyl Cysteine, NMDA: N-methyl-d-aspartate, MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil, SGC: SGC-CBP30.