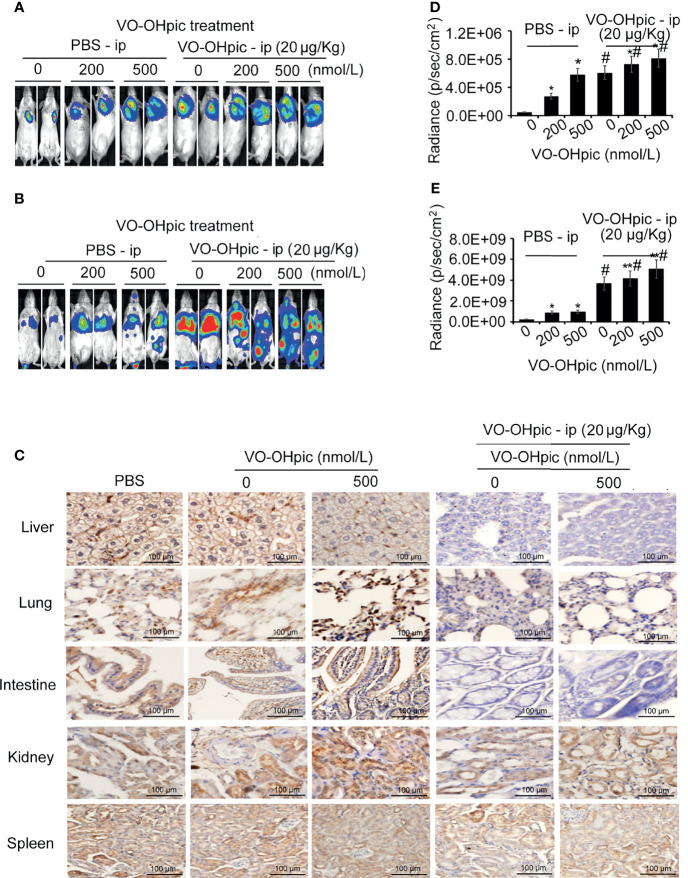
Figure 5.
PTEN-deficient breast cancer cells showed greater proliferation and metastasis potential in hosts with low PTEN function. 4T1-luc cells treated with VO-OHpic were inoculated via the breast fat pad or tail vein into Balb/c mice intraperitoneally injected with VO-OHpic, to establish a local model (A) and an organ metastasis model (C). Flux intensity of breast tumors in situ (B) and distant metastases (D) were significantly increased in mice treated with PTEN inhibition in vivo and simultaneous inoculation of PTEN-deficient 4T1-luc cells, compared with mice treated with cellular or in vivo PTEN inhibition alone. PTEN protein expression levels in the lung, liver, intestine, and kidney were observed by immunohistochemistry under light microscopy (original magnification, 20×) (E). Compared with 0 nmol/L VO-OHpic group, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01. Compared to PBS - ip group, # P<0.01.