Figure 1. Schematic of the plant EV isolation and small RNA (sRNA) detection.
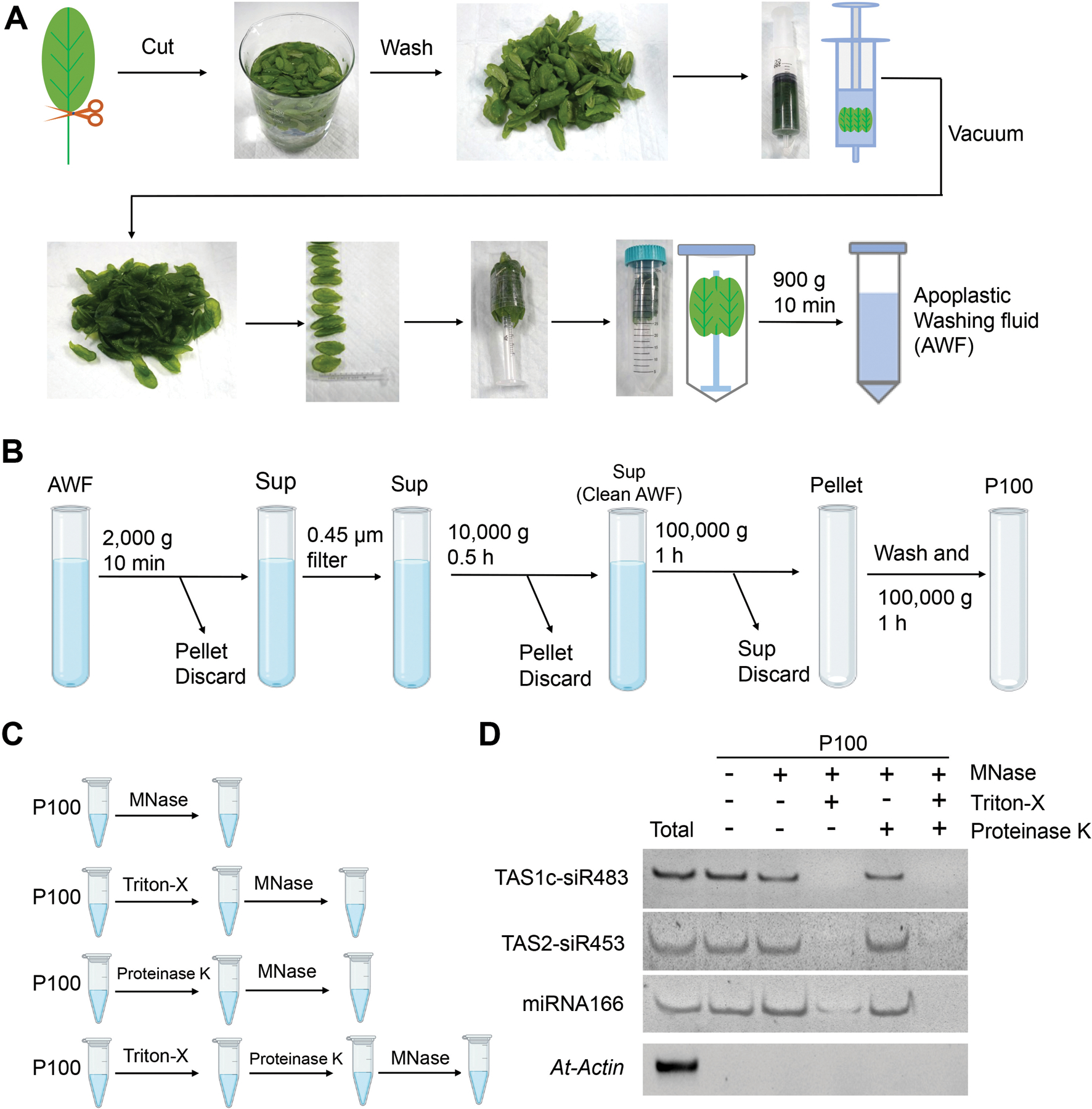
(A) Images show the various steps in apoplastic washing fluid (AWF) isolation from Arabidopsis (detached leaves protocol, Method 1 in Figure 2). The distinct proximal (petiole) part of leaves was removed using scissors, and the distal (blade) zones of leaves were collected. The leaves were placed in a syringe and gently vacuumed with infiltration buffer. The syringe with taped leaves was placed into a 50 ml conical tube, and then centrifuged at 900 × g to collect the apoplastic washing fluid. (B) Schematic of EVs isolated by differential centrifugation of AWF from Arabidopsis. The clean AWF was centrifuged at 100,000 × g to obtain the P100 EV fraction. Sup, Supernatant. (C) Schematic of EVs treated with micrococcal (MNase) and proteinase K. (D) EV-enriched sRNAs (TAS1c-siR483, TAS2-siR453 and miRNA166) were detected in nuclease-treated EVs or proteinase plus nuclease-treated EVs. Actin gene was used as the control. The “total” lane indicates total RNAs from leaves.
