Scheme 1.
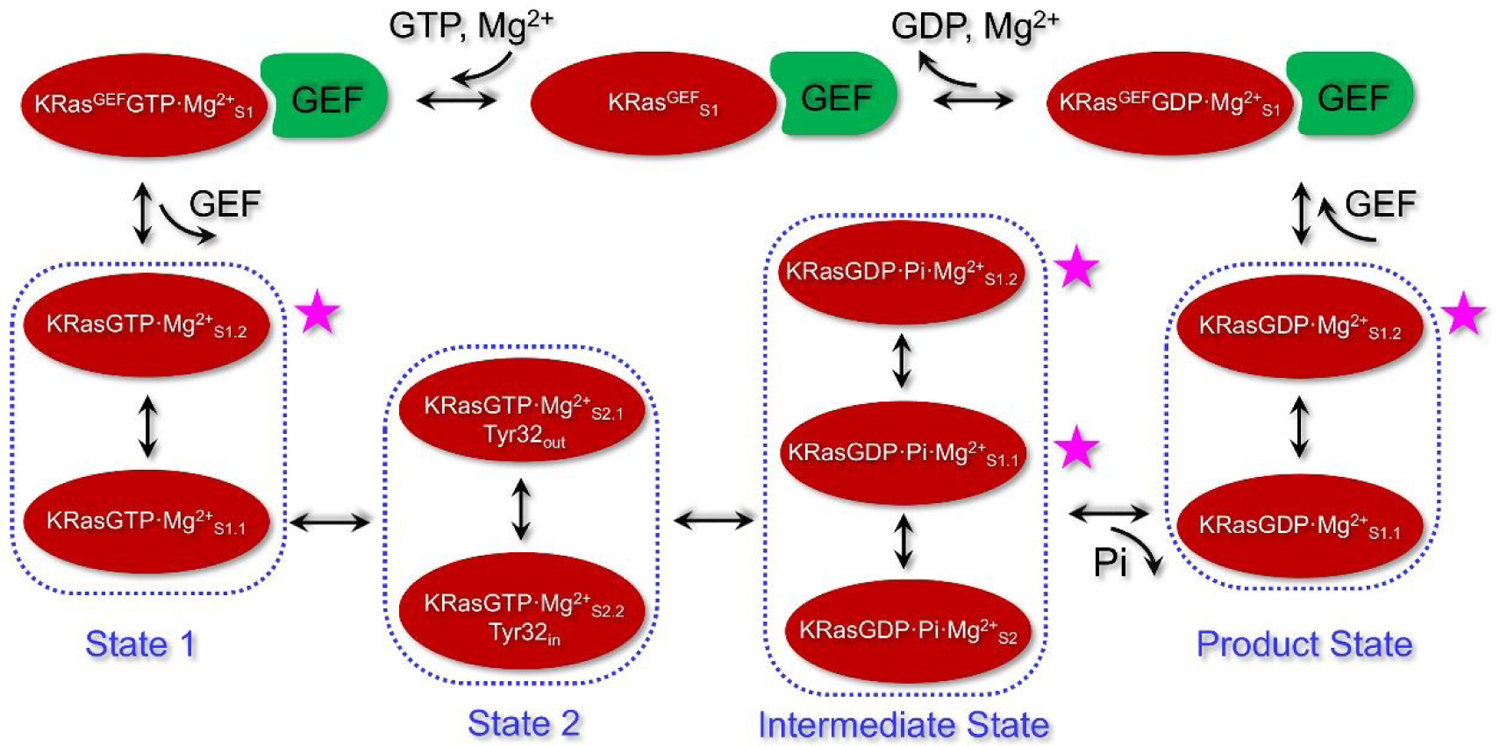
An illustration for the processes of GTP hydrolysis and exchange in KRas, including the specific substates defined based on the conformations from REMD simulations. State 1 and State 2 of KRasGTP·Mg2+ include substates KRasGTP·Mg2+S1.1 and KRasGTP·Mg2+S1.2, as well as KRasGTP·Mg2+S2.1 and KRasGTP·Mg2+S2.2, respectively. The intermediate state of KRasGDP·Pi·Mg2+ is compose of three major substates S2, S1.1 and S1.2. After Pi is released, KRasGDP·Mg2+S1.1 is the most stable product substate. KRasGDP adopts the S1.2 substate to complex with GEF and forms the conformation of KRasGEFGDP·Mg2+S1. Release of GDP and Mg2+ leads to the KRasGEFS1 substate. Binding of the next GTP forms the conformation of KRasGEFGTP·Mg2+S1. Dissociation of GEF leads to State 1 of KRasGTP·Mg2+ in solution. The four high-energy substates, marked with the purple stars, could serve as the potential drug targets.
