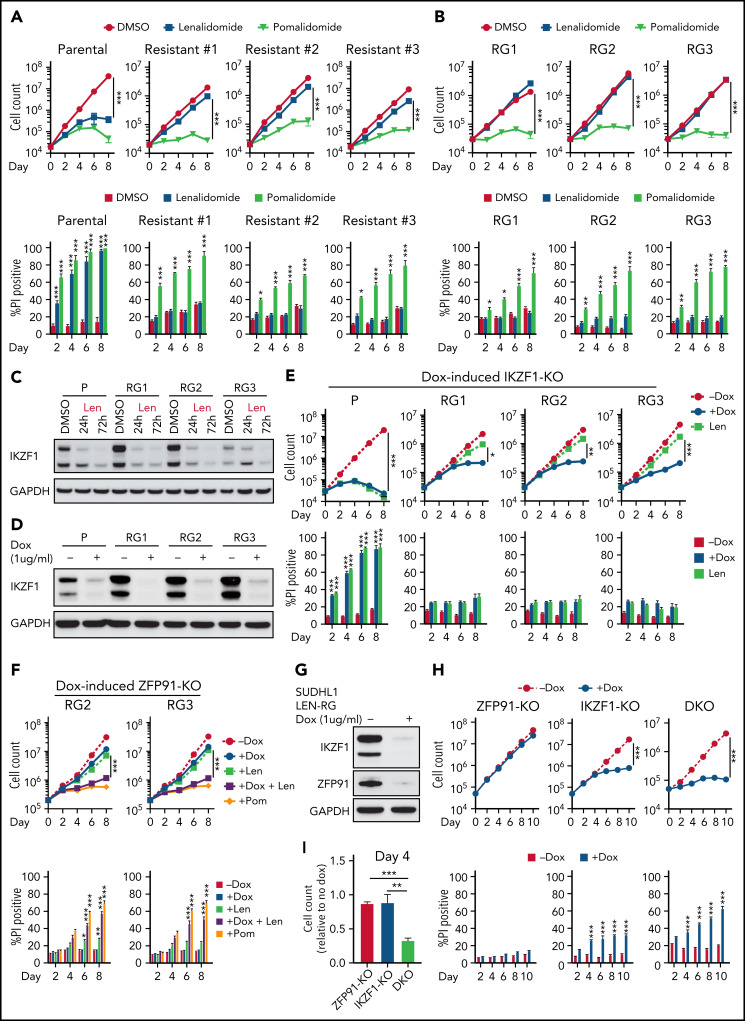
Figure 2.
Acquired lenalidomide-resistant TCLs are tolerant to IKZF1 loss but remain sensitive to pomalidomide-induced inactivation of both IKZF1 and ZFP91. (A-B) Cell count and percent PI+ in SU-DHL-1 parental, len-resistant (A), and len-regrown (RG) cells (B) treated with 1 μM IMiDs or DMSO. The experiment was performed in triplicate and replicated twice. Data are presented as mean plus or minus SD. Comparisons are by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. (C) Western blot for IKZF1 in SU-DHL-1 parental and len-regrown cells upon exposure to 1 μM len for 24 or 72 hours. (D) Western blot for IKZF1 in SU-DHL-1 parental and len-regrown cells with dox-induced IKZF1 knockout. (E) Cell count and percent PI+ in SU-DHL-1 parental and len-regrown cells with dox-induced IKZF1 knockout. The experiment was performed in triplicate and replicated twice. Data are presented as mean plus or minus SD. Comparisons are by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. (F) Cell count and percent PI+ in SU-DHL-1 len-regrown cells with dox-induced ZFP91 inactivation in combination with 1 μM lenalidomide treatment and compared with 1 μM pomalidomide treatment. The experiment was performed in triplicate and replicated twice. Data are presented as mean plus or minus SD. Comparisons are by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. (G) Western blot for IKZF1 and ZFP91 in SU-DHL-1 len-regrown cells with dox-induced knockout of both IKZF1 and ZFP91. (H-I) Cell count and percent PI+ in SU-DHL-1 len-regrown cells with dox-induced IKZF1 and ZFP91 single or double knockout (DKO). Shown in (I) is relative cell count at day 4 compared with no dox. The experiment was performed in triplicate and replicated twice. Data are presented as mean plus or minus SD. Comparisons are by 2-tailed Student t test. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001. Dox, doxycycline.