FIGURE 9.
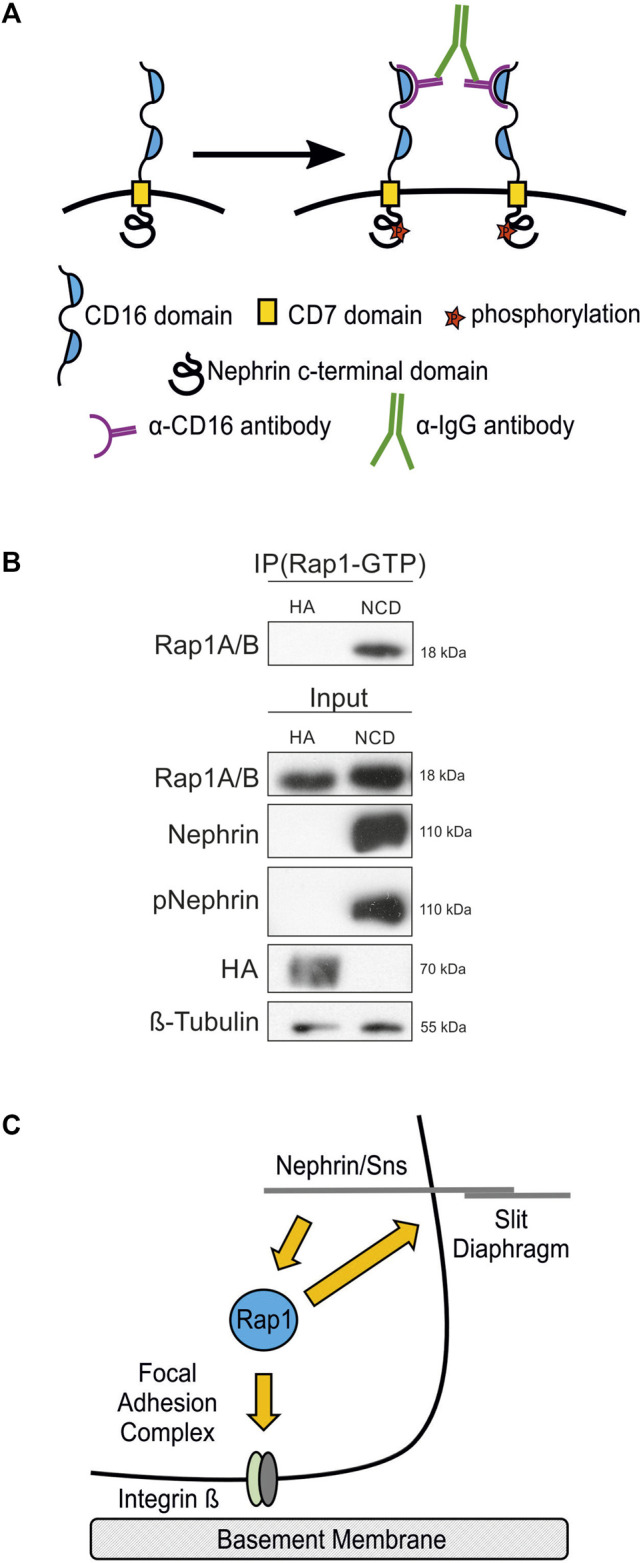
Nephrin activation results in increased active Rap1 in human podocytes. (A) A nephrin clustering assay was performed by adding anti-CD16 antibody and secondary anti-IgG antibody to the media of cultured podocytes, which induces clustering of nephrin proteins followed by recruitment of Src kinases and consecutive phosphorylation of nephrin on tyrosine residues. (B) Immunoblot with antibodies specific for Rap1A/B following immunoprecipitation (IP Rap1-GTP) with an antibody specific for active Rap1A/B of podocyte lysates. Employed were human podocyte lines that inducibly express either chimeric CD16-CD7-nephrin cytoplasmic domain (NCD) or CD16-CD7-HA (HA) as a control following doxycycline treatment followed by clustering of nephrin. Immunoblots of these lysates were also performed with antibodies specific for Rap1A/B, nephrin, phospho-nephrin (pNephrin), HA, and β-tubulin (Input), n = 3. (C) Schematic of the hypothesis that the small GTPase Rap1 functions downstream of nephrin in signaling to integrin β at focal adhesions and in signaling at the slit diaphragm.
