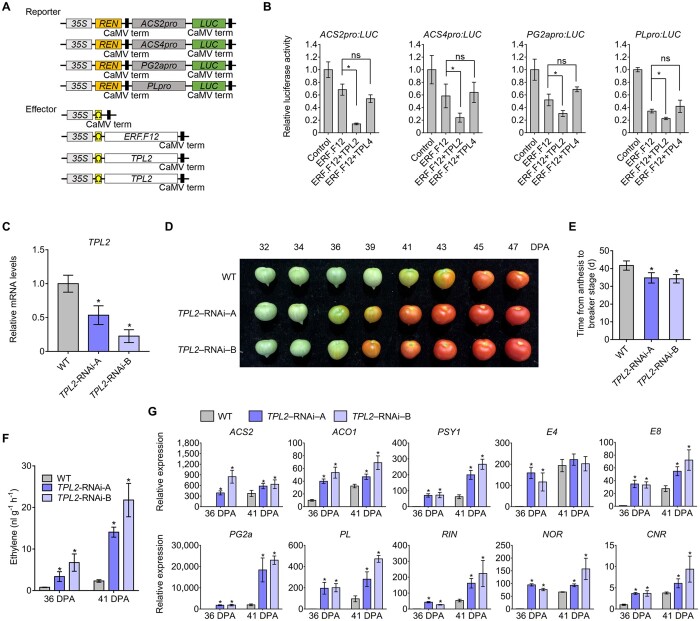
Figure 7.
TPL2 enhances the repression of transcription of ripening-related genes by ERF.F12 and represses fruit ripening. A, Schematic diagram of the double-reporter and effector plasmids used in the transient expression assay. B, Repression by ERF.F12 co-transformed with TPL2 or TPL4 of the transcription of ripening-related genes ACS2, ACS4, PL, and PG2a. The double reporter construct was co-transfected with individual effector plasmids into N. benthamiana protoplasts. Each value represents the means of six biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using Student’s t test, P < 0.05. C, Relative TPL2 transcript levels assessed by RT-qPCR in fruits at the Br stage in WT and TPL2-RNAi lines. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using Student’s t test, P < 0.05. D, Ripening phenotype of TPL2-RNAi lines. WT, TPL2-RNAi-A, and TPL2-RNAi-B fruits at 32, 34, 36, 39, 41, 43, 45, and 47 DPA are shown. E, Time from anthesis to the Br stage in WT, TPL2-RNAi-A, and TPL2-RNAi-B lines. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using Student’s t test, P < 0.05. F, Ethylene production in WT, TPL2-RNAi-A, and TPL2-RNAi-B fruits at 36 DPA and 41 DPA. Values represent means of measurements of at least 15 individual fruits. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using Student’s t test, P < 0.05. G, Relative expression of ethylene biosynthesis genes ACS2, ACO1; carotenoid biosynthesis genes PSY1; ethylene-responsive genes E4, E8; fruit softening-related genes PG2a, PL; and ripening regulators RIN, NOR, and CNR in WT, TPL2-RNAi-A, and TPL2-RNAi-B lines. Total RNA was extracted from the indicated fruits at 36 and 41 DPA. Relative transcript levels of each gene in WT at 36 DPA were normalized to 1, with SlActin as an internal control. Data are shown as means ± sd from six biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using Student’s t test, P < 0.05.