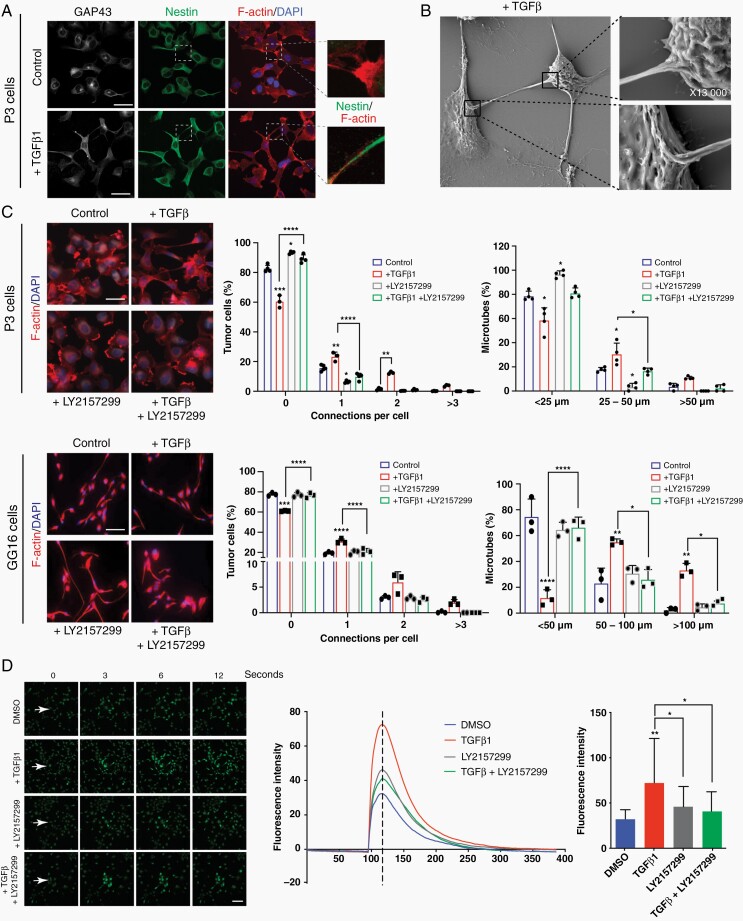
Fig. 2.
TGF-β promotes MT formation and communication via calcium signaling in GBM cells. (a) Cellular protrusions induced by TGF-β1 in P3 GBM cells are identified as MTs due to the expression of GAP43 which co-localizes with the cytoskeleton protein nestin. Scale bar 20 µm. (b) Scanning Electron Microscopy of P3 GBM cells shows that MTs connect 2 neighboring cells through cytoplasmic insertions. Higher magnifications of specific areas are provided as indicated. (c) TGF-β inhibitor LY2157299 inhibits MT formation in P3 and GG16 GBM cells. Immunofluorescence staining for F-actin is shown. Quantification of connections per cell and MT length is presented. Scale bar 10 µm. Statistically significant differences of experimental groups compared to the control are shown on top of the respective bars. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001. (d) Calcium exchange between tumor cells is significantly increased upon TGF-β stimulation and inhibited by LY2157299 in P3 GBM cells. Fluorescence intensity represents the intensity of the calcium signal. The images were taken seconds following the laser injury as indicated. The bar graph represents the intensity at the time point as indicated by the dotted line in the curve diagram. Scale bar 30 µm. *P < .05; **P < .01. Abbreviations: GBM, glioblastoma; MT, microtube; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta.